What Is Negative SEO?
Negative SEO (sometimes known as adverse SEO) is a malicious attempt to harm a business’s visibility in search engine results, typically with the aim of stealing its keyword rankings and traffic.
The idea is to make the target website look like it’s using SEO spam tactics that violate search engine policies. And therefore trigger the search engine into suppressing its results.
Or make the business look bad to human users. So they don’t click through.
Negative SEO is unethical and can be illegal in certain cases.
It also tends to be ineffective. Because search engines are getting better at spotting—and ignoring—negative SEO attacks.
For years, Google spokespeople have advised webmasters to ignore threats and attacks. And instead focus on making their site better.
So, if you notice a decline in keyword rankings or organic traffic, it’s unlikely that negative SEO is to blame.
That said, many marketers believe attacks can harm a business’s rankings and reputation. So you should be aware of the different types and how to deal with them.
7 Types of Negative SEO Attacks
Below are some of the most common types of negative SEO attacks.
We’ll explain how to identify, address, and prevent these attacks.
1. Hacking
Hackers can gain unauthorized access to a website and harm its SEO in a variety of ways.
For example, they might:
- Delete or deface your content
- Redirect your URLs to spammy pages
- Inject malicious code that harms your users
This type of negative SEO isn’t always obvious.
To protect your site, you should:
- Regularly scan your website with security software
- Enable security alerts in Google Search Console
- Investigate any sudden declines in your SEO results
With Semrush’s Position Tracking tool, you can get alerts when rankings drop.
After setting up the tool, click the bell icon at the top.
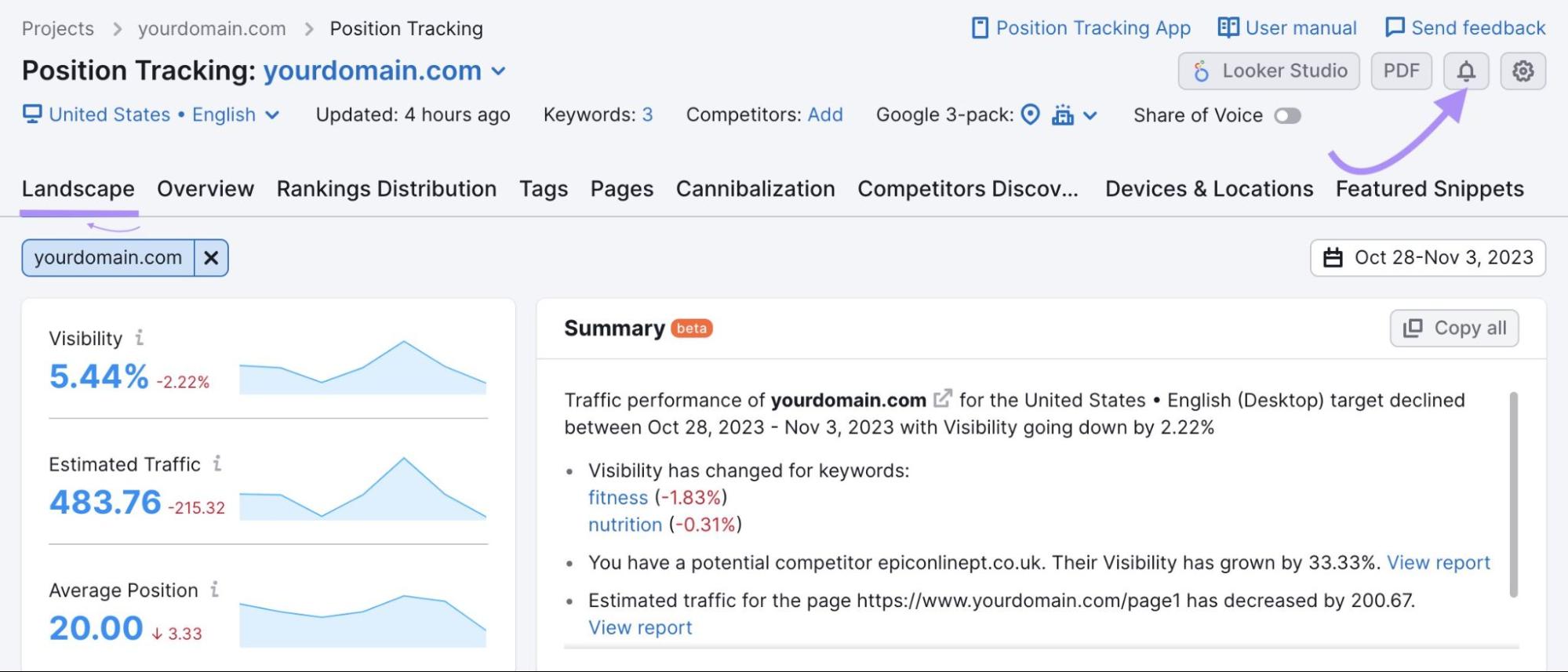
Then, create a trigger like this:
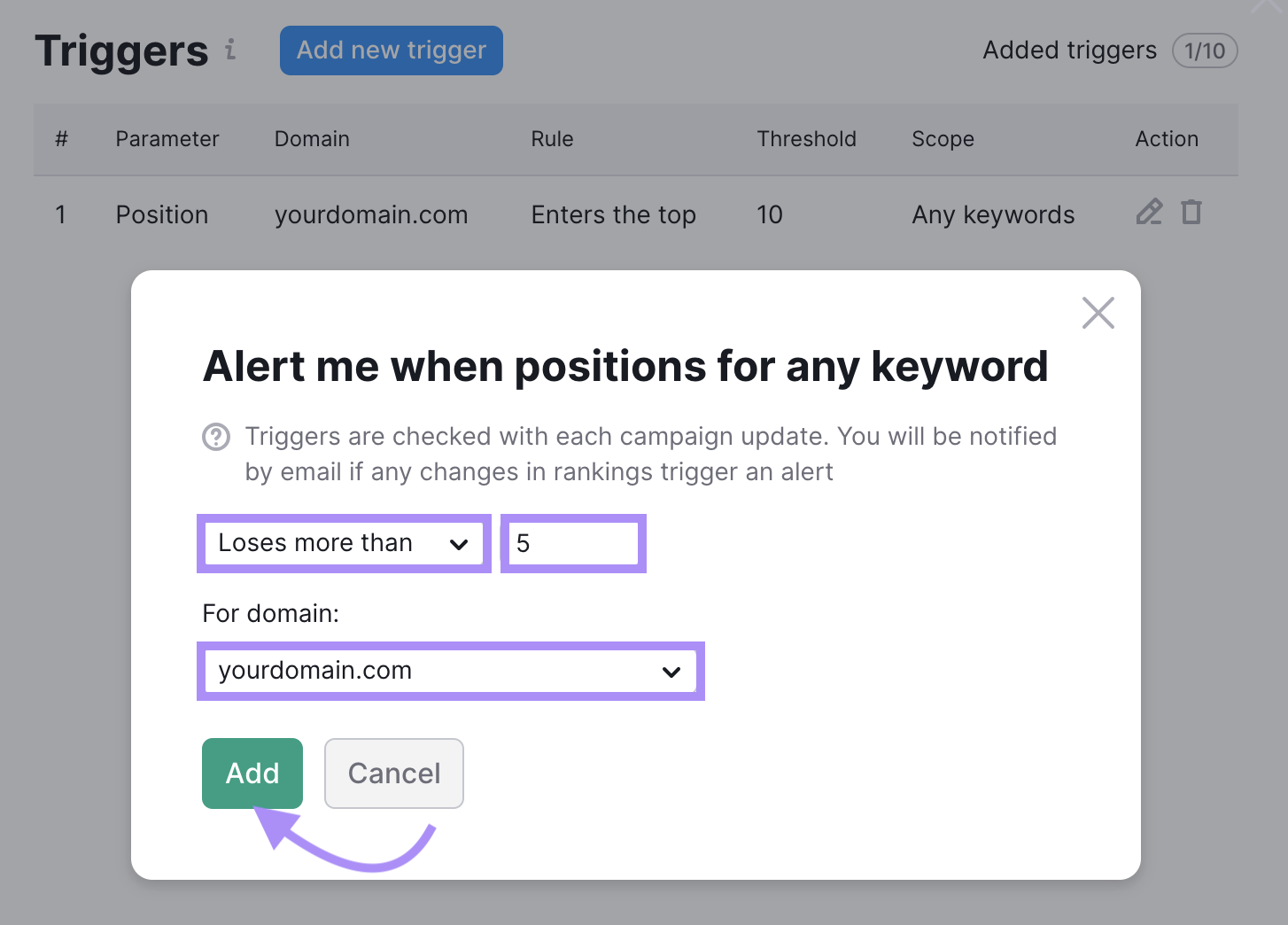
Just remember that drops are rarely due to negative SEO attacks. There are many other things that can hurt your rankings.
2. Link Removals
Certain kinds of backlinks (links from other sites) can benefit your SEO. So unscrupulous competitors might try to remove them.
How?
By contacting the referring site and asking them to remove the link. While pretending to act on your business’s behalf.
To monitor lost backlinks, use Semrush’s Backlink Audit tool.
After setting it up, go to the “Lost & Found” report.
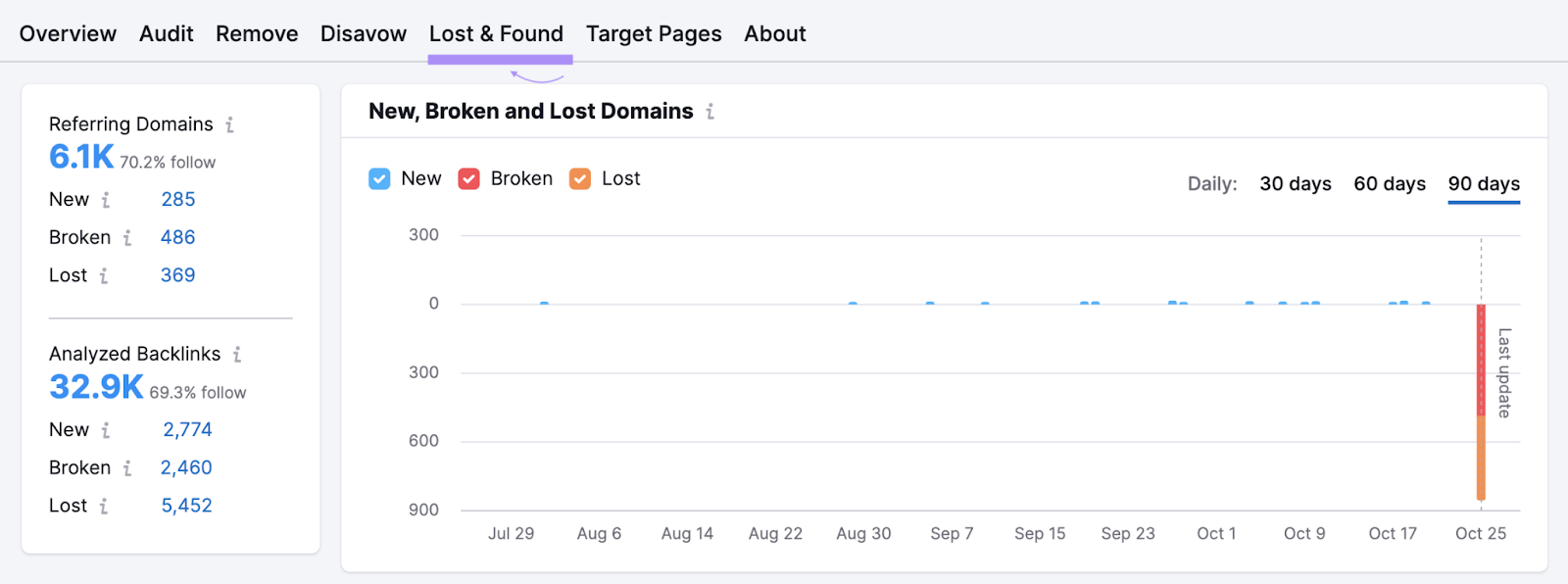
Scroll down and click “Lost” to see backlinks you’ve lost in the past three months.
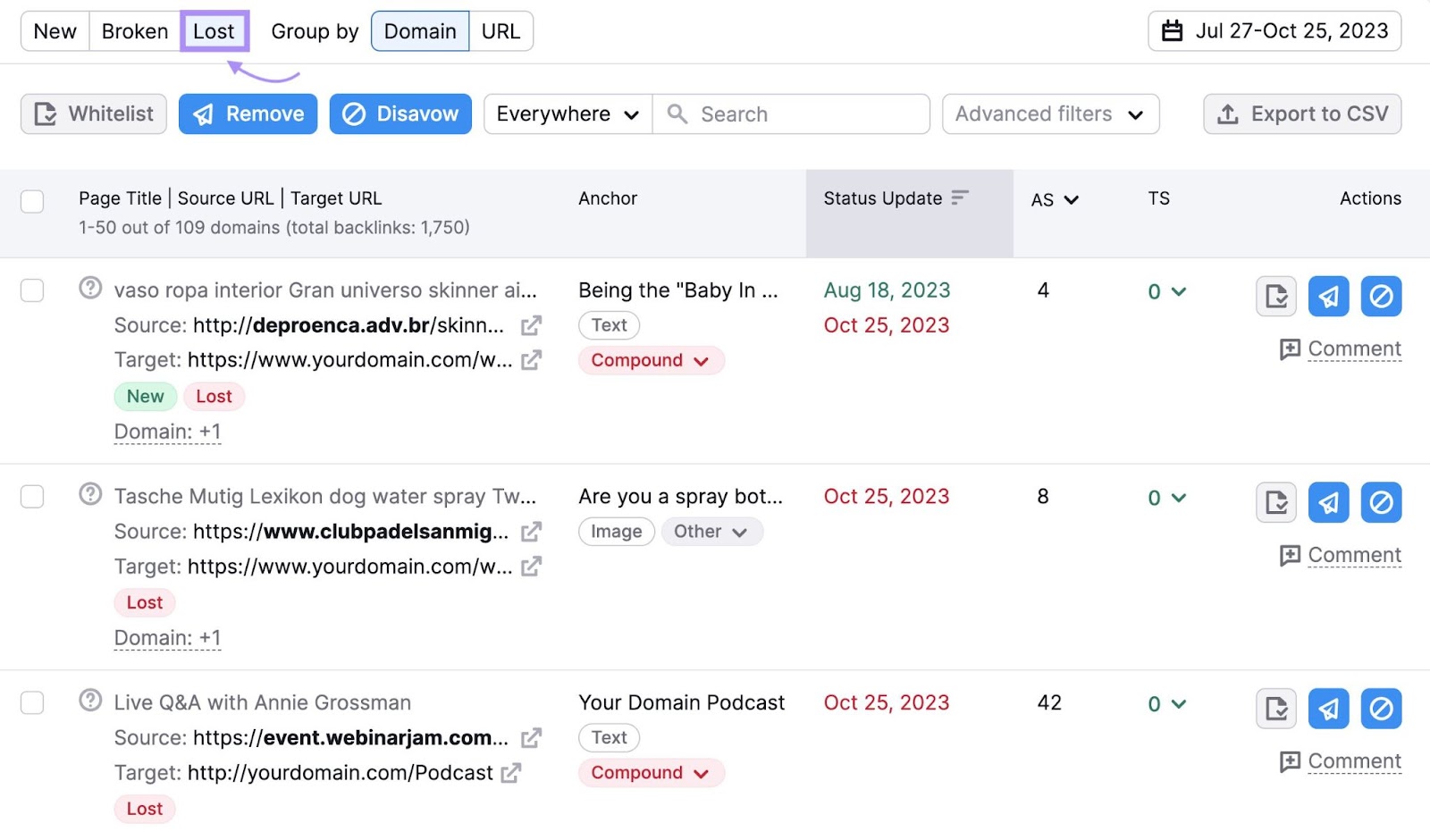
If you lose a potentially valuable backlink (due to a negative SEO attack or other reason), consider reaching out to the site. And kindly asking them to reinstate it.
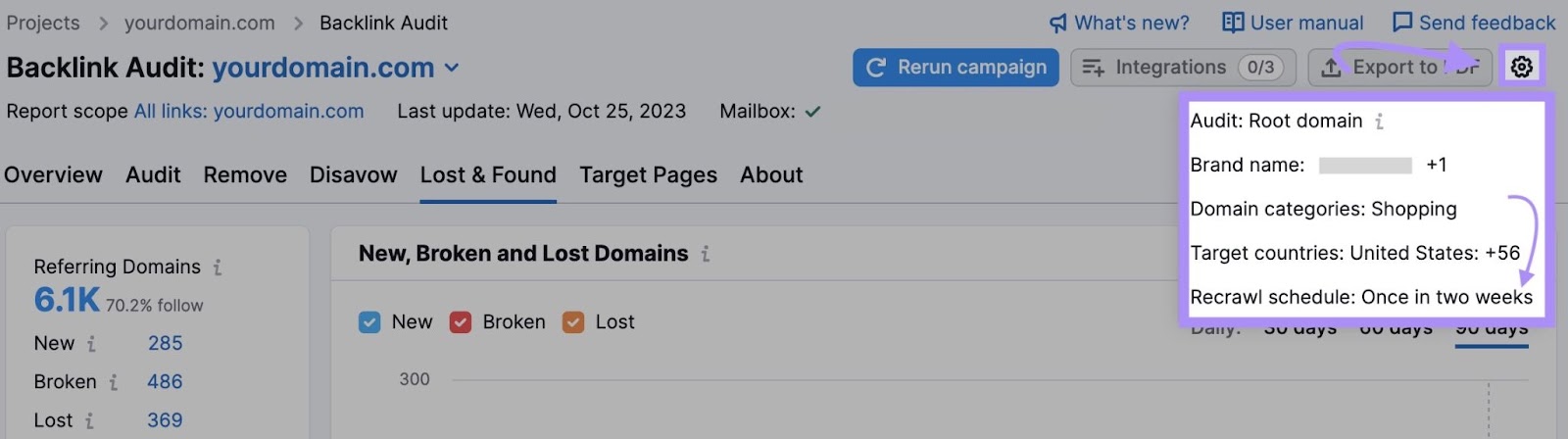
To ensure you don’t miss lost backlinks in the future, set up automatic recrawls.
Click the cog icon and open the “Recrawl schedule.”
Decide whether you want to check your backlinks every week, two weeks, or month.
Then, check the box to enable email alerts. And exit to save your settings.
3. Malicious Link Building
Malicious link building is the process of building spammy links to a target site, with the goal of making search engines penalize the target site.
For example, Google’s link spam policies state that websites should not build keyword-rich links across various sites.
So an unscrupulous marketer might use negative SEO services to do exactly that. Making sure all the links point to a competitor’s domain.
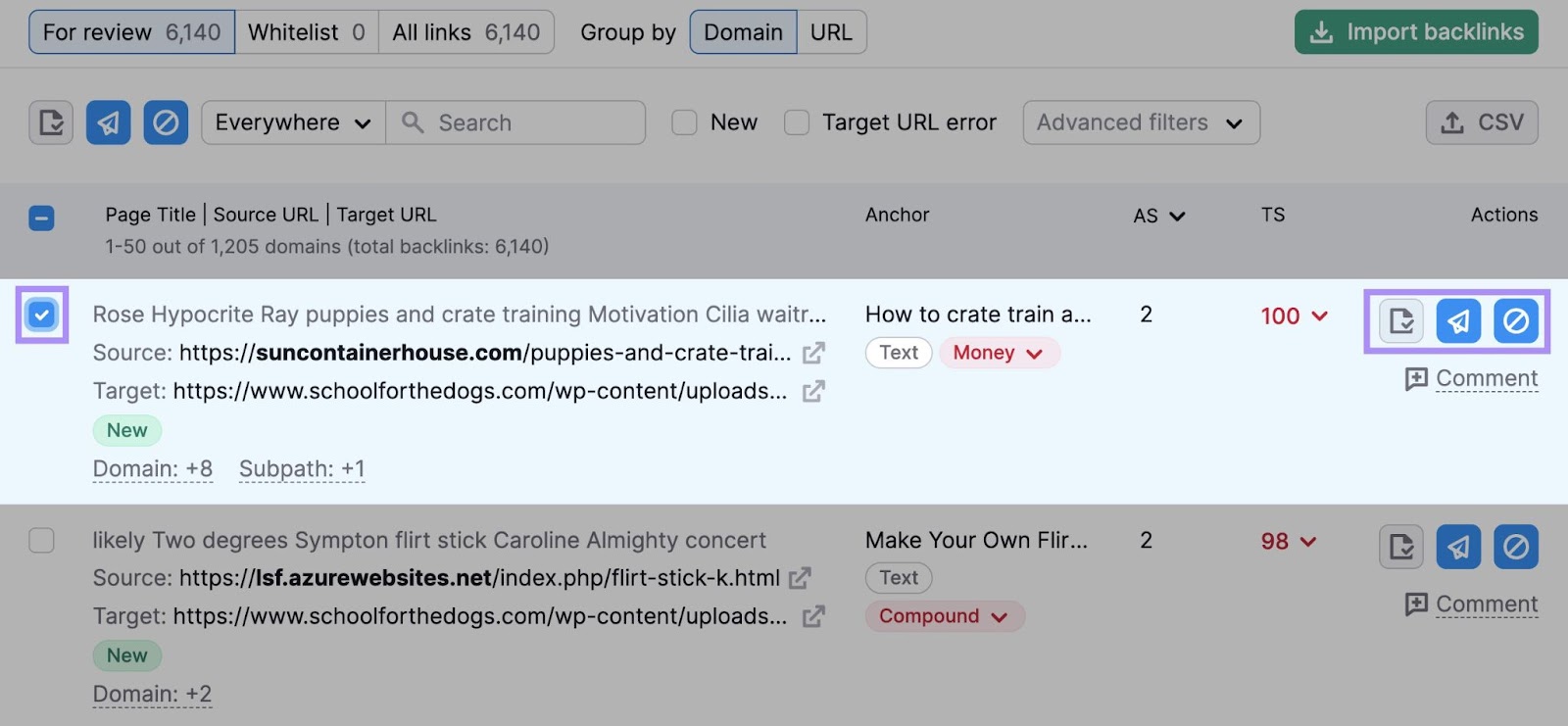
To see if you’re a victim, use Semrush’s Backlink Audit tool.
The tool finds backlinks to your site. Then analyzes 45+ markers to assign each one a Toxicity Score (TS) out of 100.
Go to the “Audit” tab to see all your suspicious links.
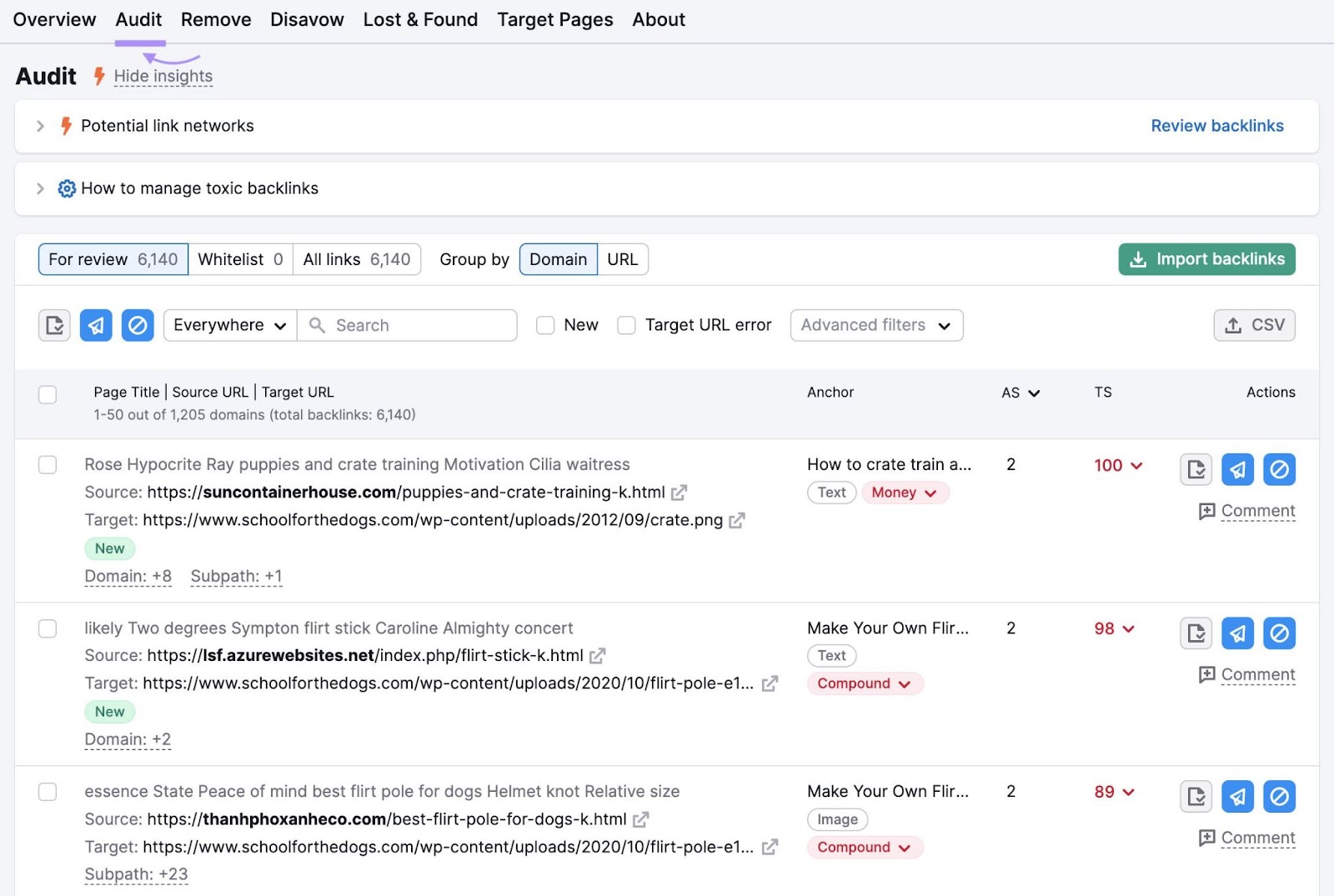
Analyze each backlink to determine whether it’s harmful.
Then, send it to one of three lists (using the corresponding icon):
- Whitelist: This is where you move backlinks that you’ve deemed safe
- Removal list: From here, you can contact the referring site and ask them to remove the link
- Disavow list: From here, you can create a disavow file that asks Google to ignore the link
It’s important to note that disavowing links can do more harm than good.
Google’s John Mueller claims that malicious links should not harm the target site’s SEO. And should simply be ignored.
4. Content Scraping
Content scraping is the process of copying content from a target site and publishing it elsewhere without permission.
When Google encounters duplicate content, it will usually pick just one version to display. Because it doesn’t want to deliver near-identical results to its users.
And it might show the plagiarized version, rather than the original. Meaning that the target site suffers from organic traffic losses.
To see if your content’s been scraped, consider a service like Copysentry. It automatically monitors the web for copies of your pages. And alerts you of any hits.
If your content is plagiarized, contact the webmaster and ask them to remove the content.
If unsuccessful, you can report the issue to Google, submit a DMCA notice, or take legal action. Consult a qualified legal professional about your legal options before taking legal action.
Further reading: SEO Plagiarism: How to Find and Prevent Copycat Content
5. Smear Campaigns
A smear campaign is an effort to spread false and damaging information about a person or business.
For example, the perpetrator might:
- Write a defamatory blog post
- Create fake social profiles for impersonation purposes
- Spread rumors via online communities like Reddit
- Submit baseless DMCA notices (copyright infringement complaints)
- Share false information with influencers in your niche
These activities can harm your business’s reputation. Potentially meaning that Google’s less likely to rank you highly—and users are less likely to click your results.
To protect your business, respond appropriately to any formal complaints you receive. And keep an eye on your brand mentions (online references to your brand name).
The Brand Monitoring app makes it easy.
Just enter the name of the brand you want to track.
Then, go to the “Email notifications” tab and click “Set up email notifications.”
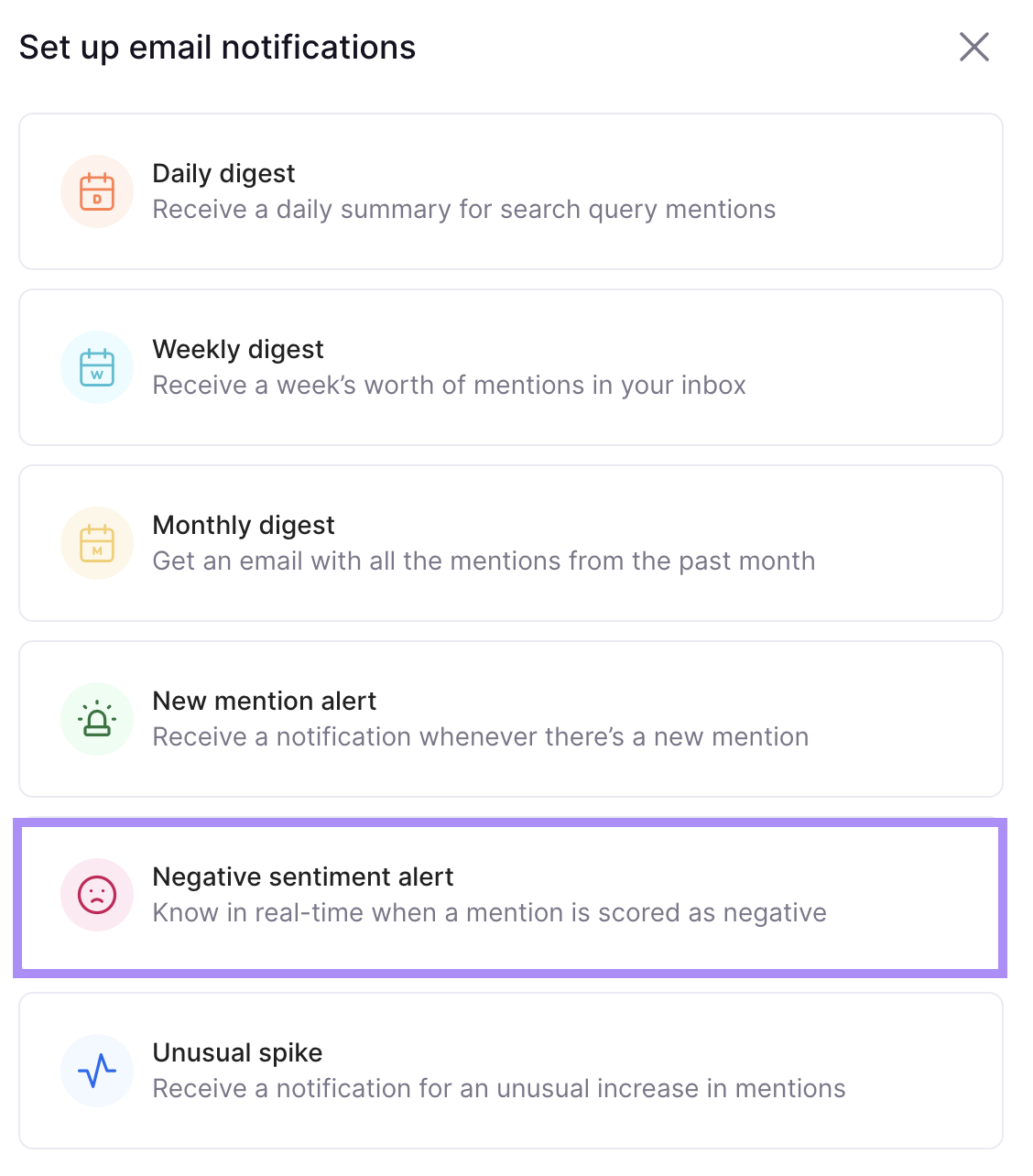
We recommend setting up a “Negative sentiment alert.” So you’re immediately notified when someone says something bad about your brand.
But you might want alerts for other mentions, too.
To view all your mentions in one place, head to the “Mentions” tab.
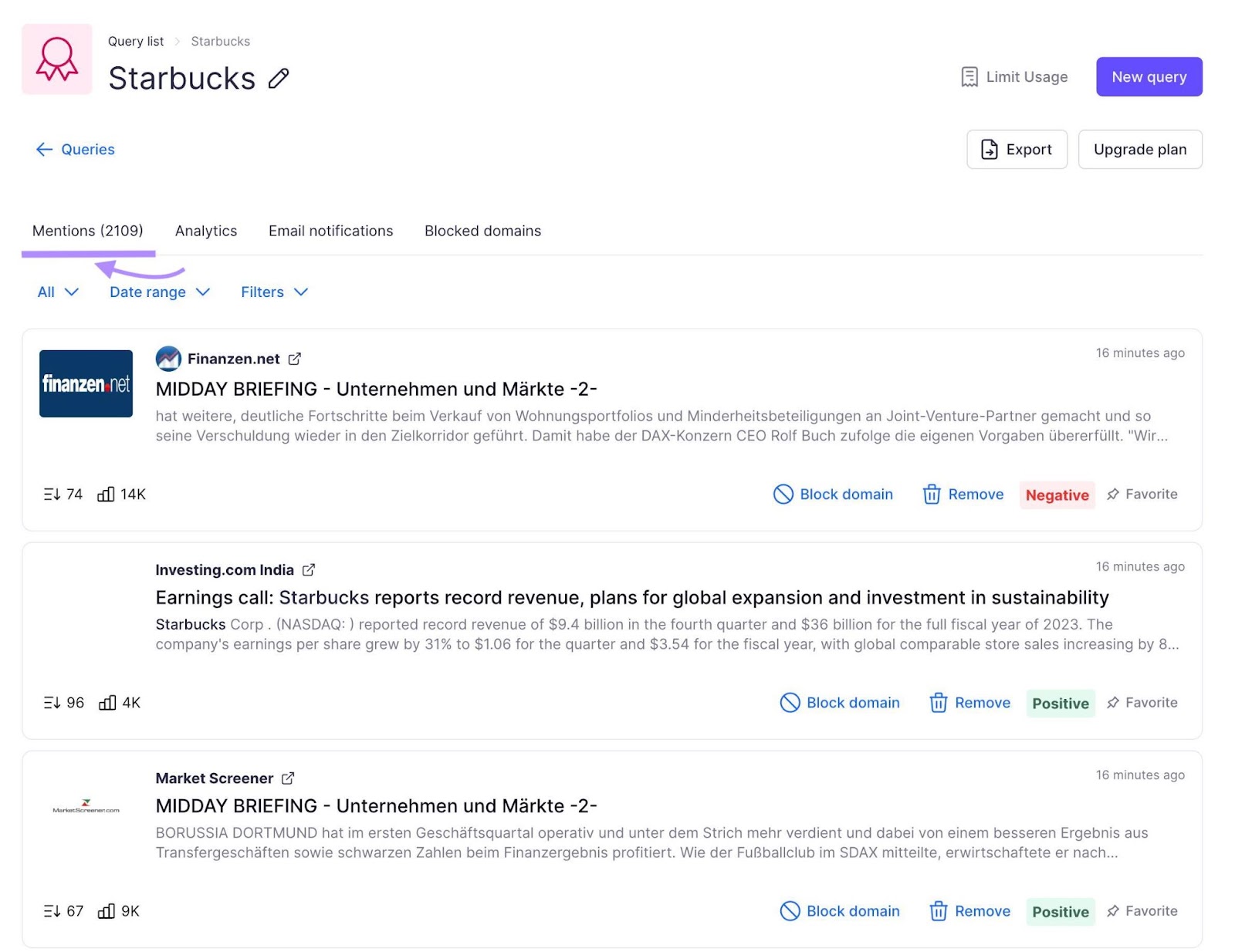
Just remember:
Not all negative mentions result from negative SEO attacks. So you need to choose your course of action carefully.
For example, if you’re dealing with a genuine disgruntled customer, you might need to contact them and offer a friendly resolution.
But if you’re dealing with a malicious attack, you might need to consider more serious action.
Further reading: A Beginner’s Guide to Online Reputation Management
6. Review Bombing
Review bombing is the act of posting high volumes of fake, negative reviews for a business.
Bad ratings can appear in Google results. And discourage users from clicking through.
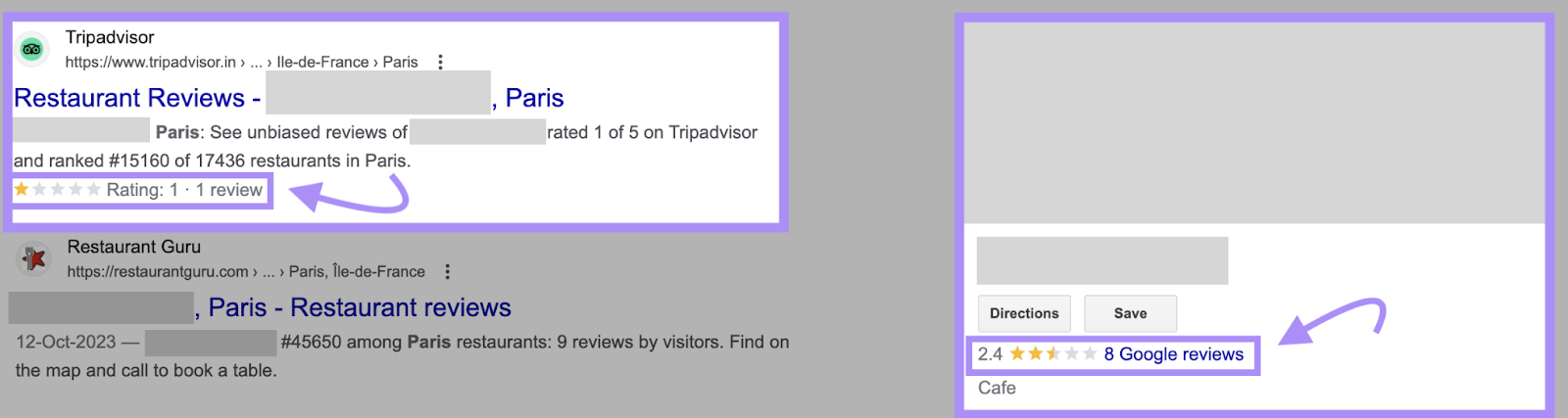
Plus, Google ratings play an important role in local SEO. The top-ranking map results tend to have high average scores.
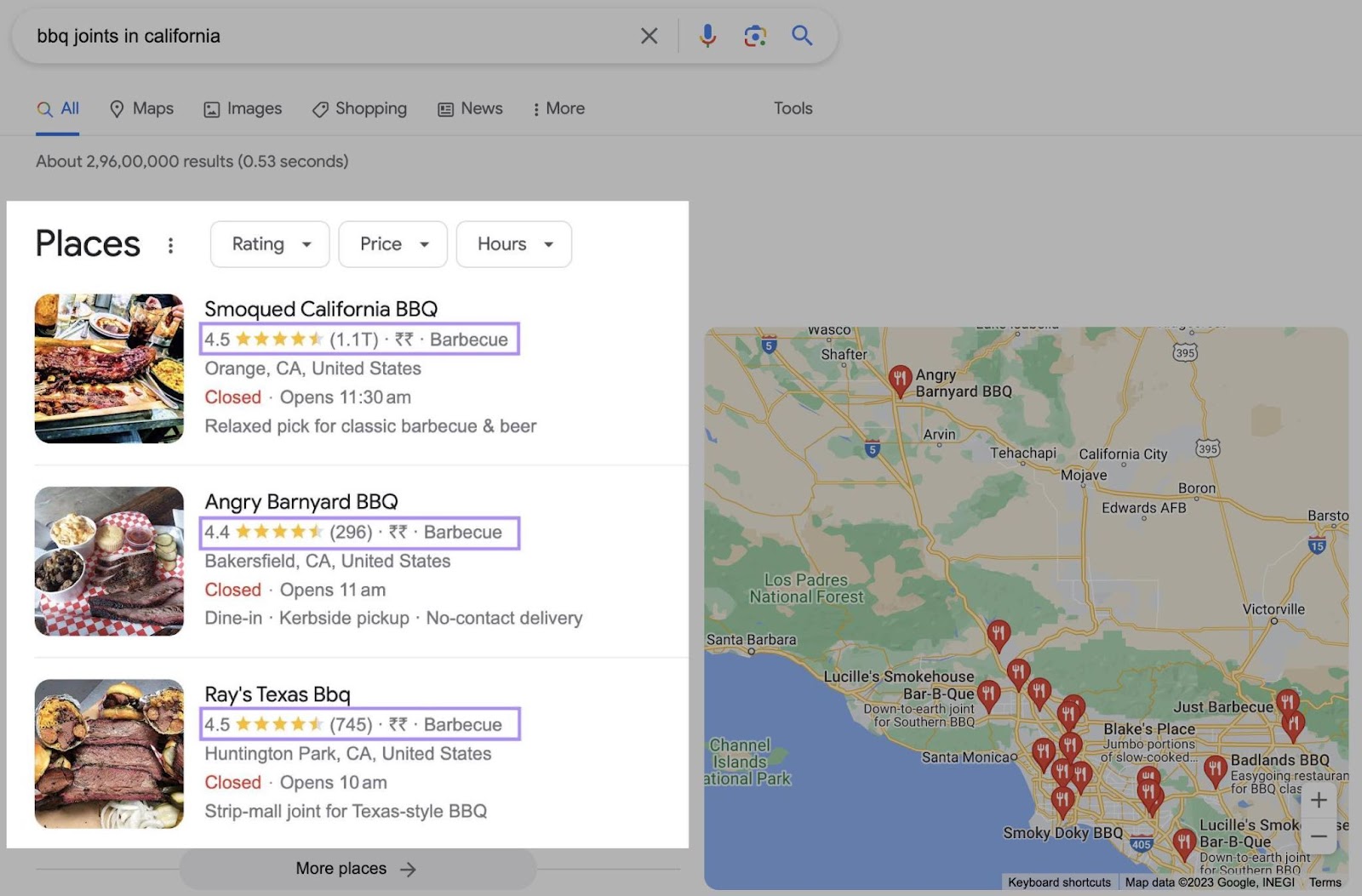
Google uses automated spam detection in an attempt to remove fake reviews. But it’s a good idea to monitor reviews manually. So you can take immediate action if anything’s missed.
To check your Google reviews more easily, use Semrush’s Review Management tool.
Monitor key metrics at the top of the report.
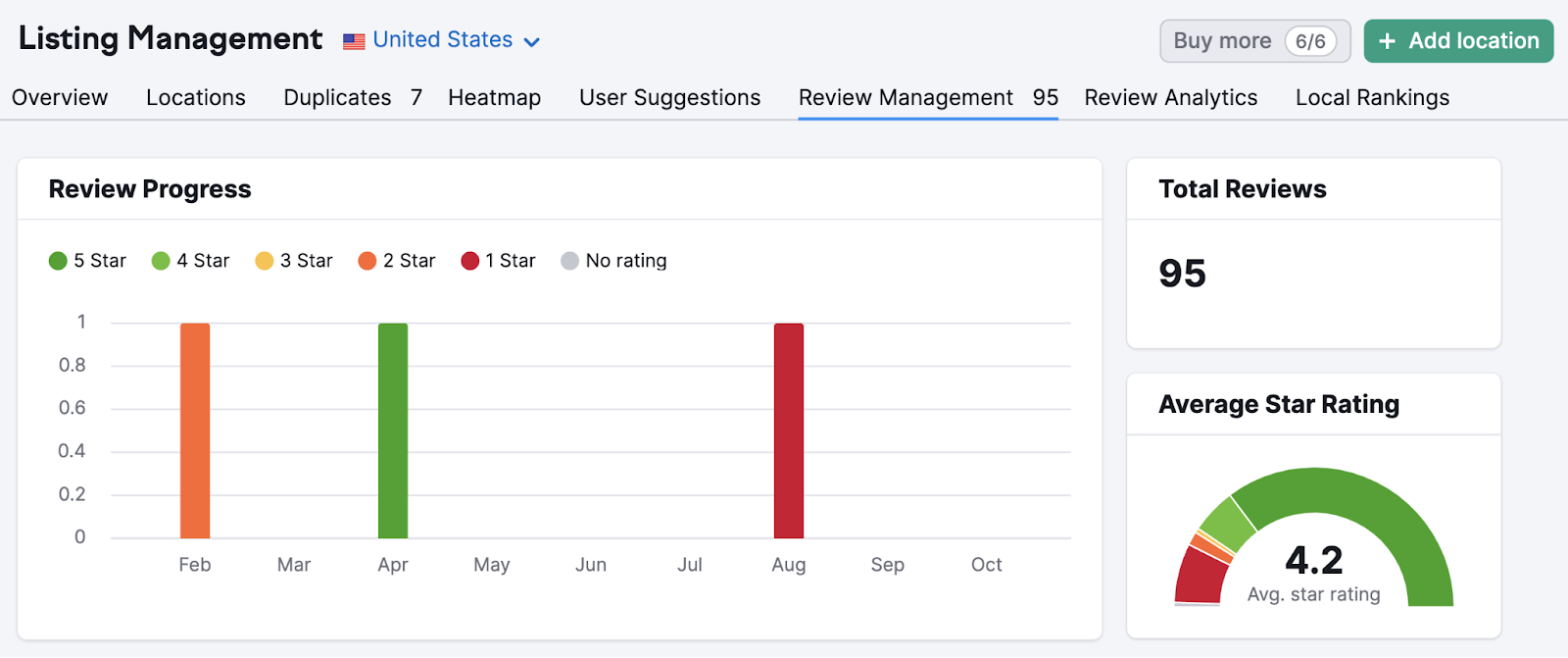
And scroll down to see individual reviews.
If you receive a fake review (or any other review that violates Google policies), you can request its removal via Google Business Profile.
Other review platforms should have a reporting feature, too.
7. Unauthorized Hotlinking
Hotlinking allows webmasters to load media (e.g., images) directly from another site rather than hosting it on their own site’s server.
Excessive and unauthorized hotlinking is used as a negative SEO attack. Because it puts strain on the host site’s servers, which can slow the site’s speed. And ultimately lead to lower rankings.
This is a type of attack called “bandwidth theft.”
There are a couple of ways you can prevent hotlinking before it even happens, like:
- Using a plugin like All-In-One-Security for WordPress sites
- Adding the following code to your .htaccess file (change “samplesite.com” to your website URL)
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^$
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^https://(www\.)?samplesite.com/.*$ [NC]
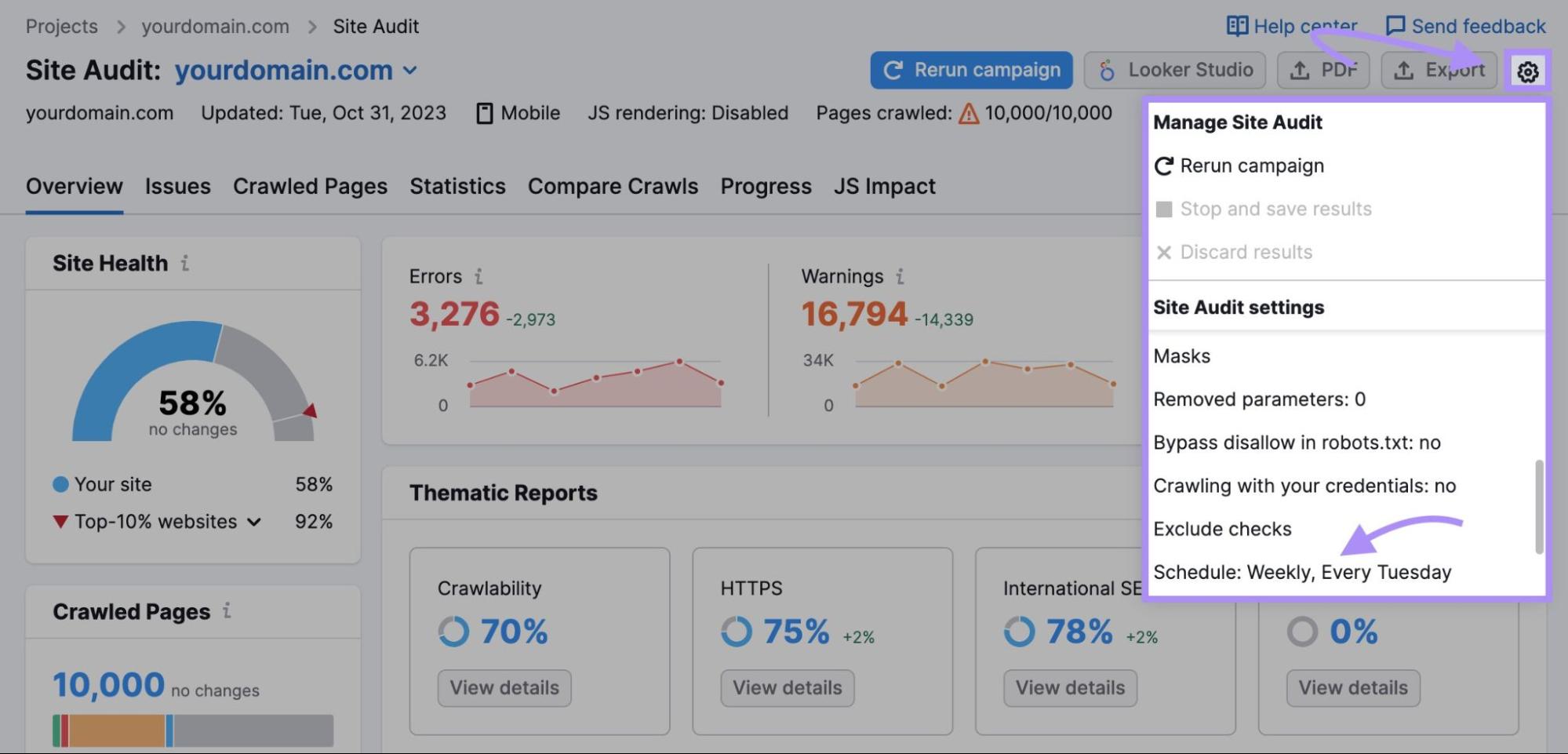
RewriteRule \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|mp3|png|pdf|zip)$ - [F]Also prevent bandwidth theft by keeping an eye on your page speed metrics with Semrush’s Site Audit tool.
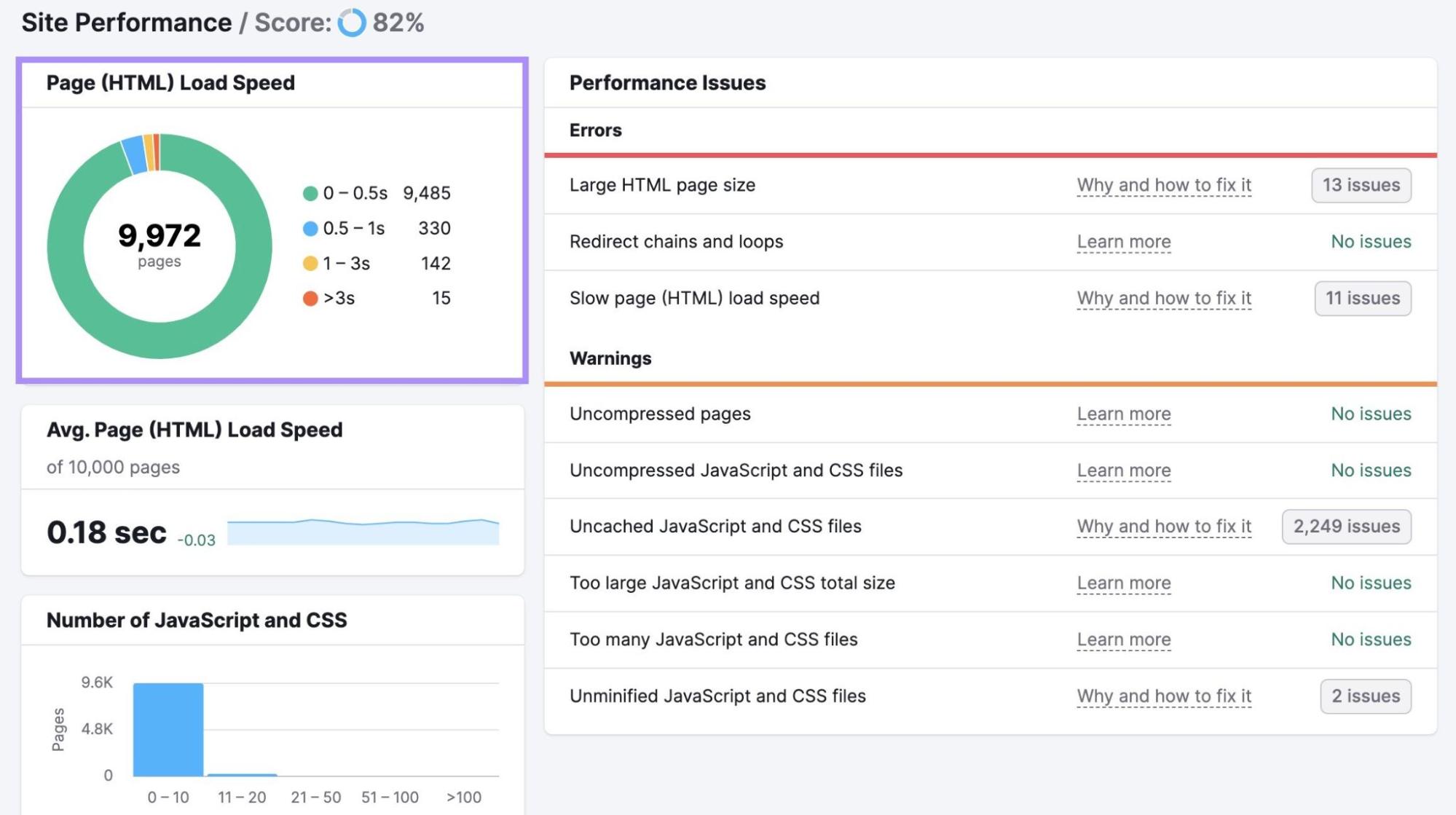
Schedule regular crawls so you can quickly identify, diagnose, and address any speed issues. (And any other technical issues on your site.)
Protect Your Business with Semrush
Semrush tools can help you identify and combat negative SEO attacks.
- Get ranking alerts with Position Tracking
- Check backlinks with Backlink Audit
- Monitor reviews with Review Management
- Analyze brand mentions with Brand Monitoring
- Track site speed with Site Audit
But they can also help you build strong rankings—and a good reputation. So you’re more immune to negative SEO.
Start your free trial today.
