Each year, voice search increasingly becomes a more dominant force to reckon with. 20% of the global online population is already using voice search, and 58% of voice users employ it to run a local business search.
Last year, we undertook a study that focused on uncovering factors that influence voice search rankings in 2019. This year, as search results vary depending on location-specific queries, we decided to check how questions about local businesses and services alter the voice search results.
The 2020 study provides unique insights into the search algorithms that are behind various voice assistants to help businesses leverage the power of voice search marketing.
About the 2020 Voice Search for Local Businesses Study
As voice search expands, the market keeps introducing more and more virtual assistants. If the previous year's study focused exclusively on Google devices, this year we’ve added Siri and Alexa to cover almost 100% of the voice assistants market:

To run the study, we employed the following devices:

The main goal of the study was to understand how different voice assistants compare to one another when it comes to returning local results and to uncover the algorithms behind them:
-
By comparing all voice assistants in regards to basic parameters like answer length and number of questions they are able/unable to answer.
-
By analyzing factors that affect how voice assistants choose what local results to return.
Key Takeaways From the Study
There are a few key insights we’d like local businesses to take away from our findings to integrate them into their overall SEO and marketing strategies:
-
Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa take up comparable market share, so businesses should aim to adapt to all three assistants whose algorithms are drastically different.
-
The average answer length for all analyzed assistants is 23 words, and Google Assistant devices return the longest answers, at 41 words.
-
Alexa cannot return results for each fourth question, implying that this is mainly a home-based device that understands voice commands but is not intended for running search queries.
-
With Google-run devices, businesses can apply the “regular” local SEO logic by polishing their Local Pack presence and tweaking their content to match the more natural language of voice search queries.
-
To be present among Apple’s Siri replies, businesses have to aim for higher Yelp ratings and more positive customer reviews. Having a 4.5/5 Yelp rating with the biggest number of reviews will turn any business into the most popular local spot in Siri’s eyes.
Comparing Various Voice Assistants
Now, diving deeper into the findings, we will reveal the specificities of different voice assistants and uncover how they choose to return certain results over others.
1. What’s the Average Answer Length?
The average answer length returned by a voice assistant for a local-intent query is 23 words:
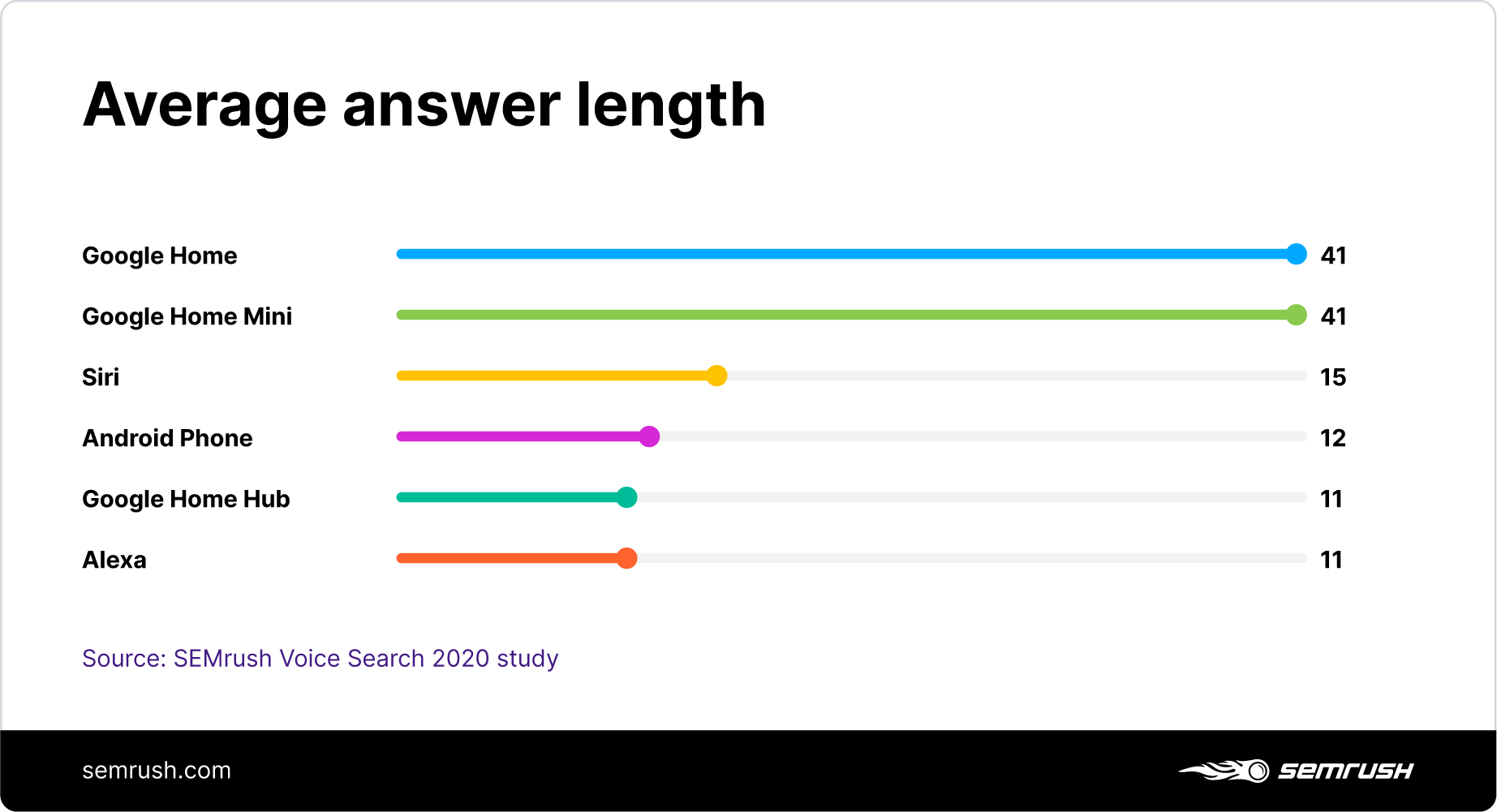
With Google devices, the presence of a screen explains the difference in word count — the Google Home/Mini’s average answer length is 3.7X of the Home Hub.
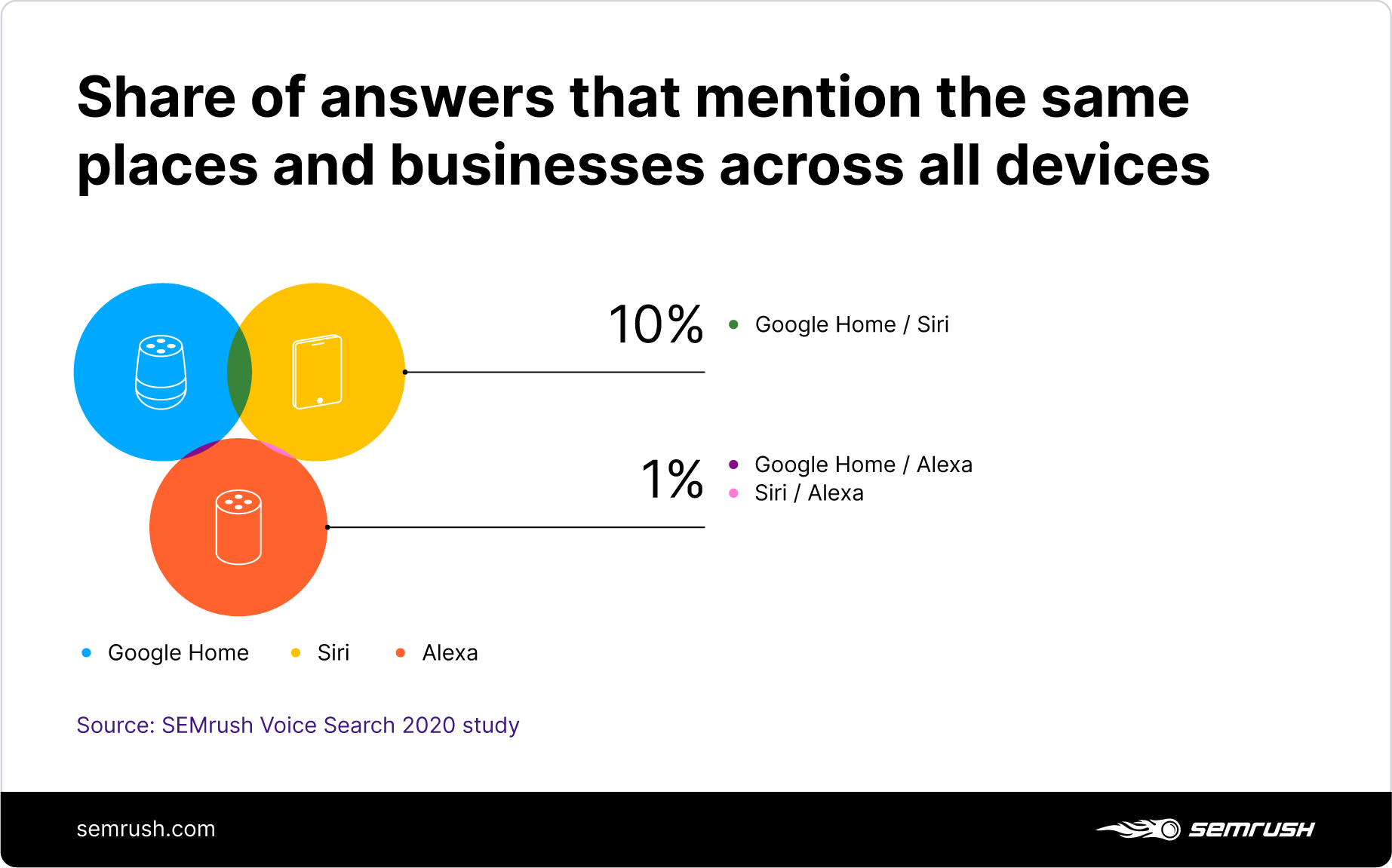
2. Do Various Google Assistants Give the Same Answers?
Google assistants do not return the same results despite having similar algorithms. The average answer match between Google Assistants stands at a mere 22% across all devices.
-
Despite the difference in the nature of the devices, the Google Home Hub and Android phone have the highest percentage of matching results at 66%.
-
Only 0.33% of the answers match between the Google Home Mini and Android phone, despite the high match between the phone and Google Home Hub.
3. The Similarity of Answers Between Google Assistants
As Google Assistant devices run on similar algorithms, namely Google search, they essentially return the same answers, using different wording.
The main reason why we see any differences has to do with screen presence/absence. A screenless device typically returns a more detailed answer, whereas those with a screen often answer with ‘Here’s what I’ve found…’ or similar, and display the information on the screen.
4. How Many Queries Voice Assistants Couldn’t Answer
Our research confirms that voice assistants are getting better at understanding users.
The average percentage of questions that are unable to be answered across all devices is just 6.3%. This is a positive trend, as Forrester’s study suggested that, just over a year ago, this figure was as high as 35%.
Of the six devices we analyzed, five of them struggled to answer only five or fewer questions out of every hundred asked, whereas Alexa struggled to answer almost one in four.
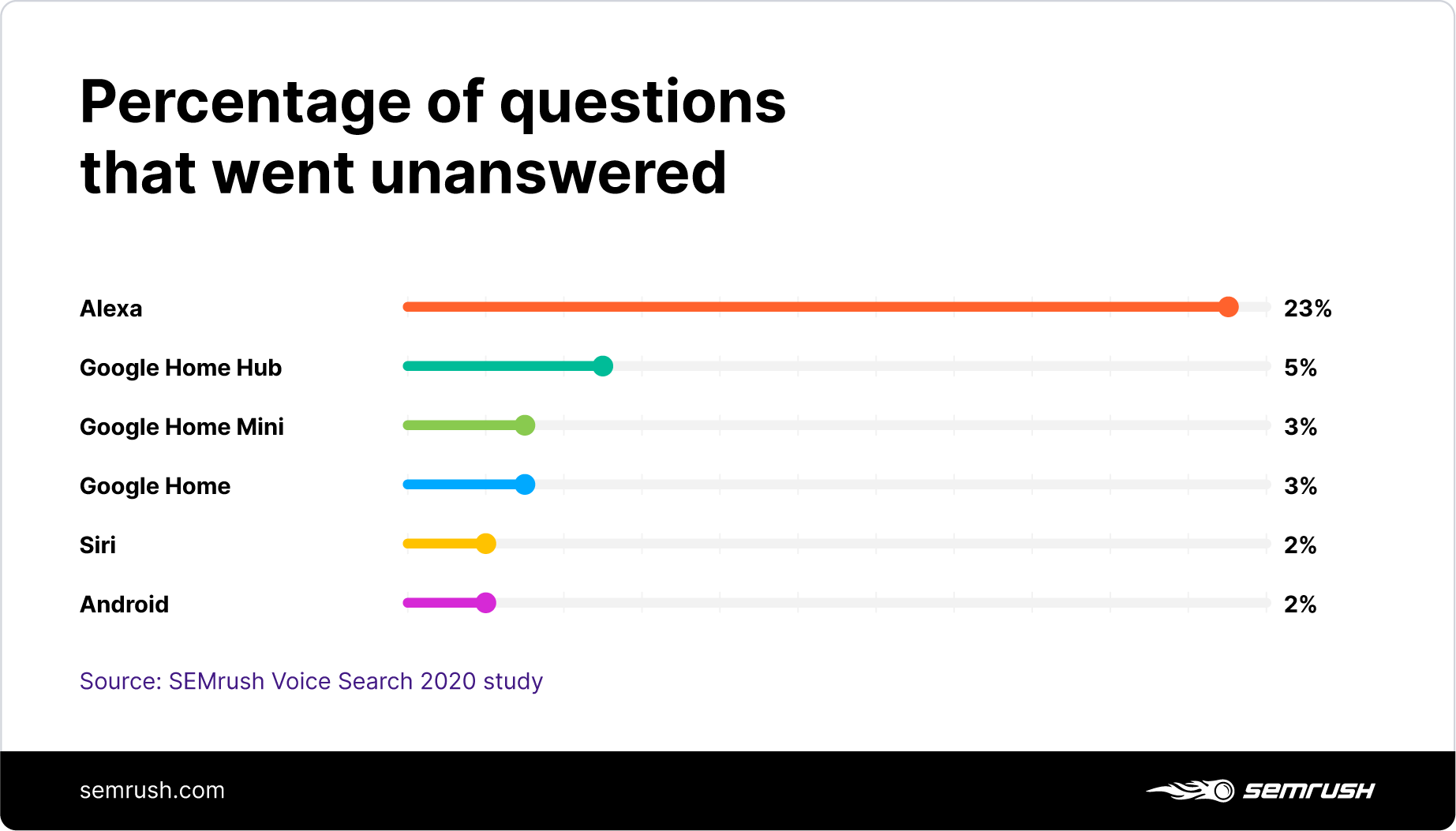
With 23% of questions unanswered, Alexa doesn’t compare to Google and Apple devices, remaining mainly a smart speaker for homes.
When it comes to search, its function was designed to help people shop, not to run web searches. It is a great assistant but when you ask it a general question, it's essentially like asking Amazon who the first king of Prussia was, what traffic conditions are like or to recommend a top-rated restaurant. Alexa wasn't designed with that in mind.
5. Are Voice Assistant Devices Recommending the Same Businesses?
Analyzing the answers given by different devices and cross-matching them with the SERP, we’ve confirmed that when it comes to local-intent queries:
-
Google devices return results based on the Local Pack SERP features.
-
Siri uses Yelp when returning results that indicate a place.
-
Unlike the rest, Alexa takes information from the Bing search engine and employs both Yelp and Yext data to give a response.

Given that various voice assistants rely on different sources of information when picking answers, they mostly return different results for the same questions.
Is Google’s Voice Search All That Personalized?
With Google’s emphasis on personalization, we decided to look at how this trend applies to voice search.
Comparing the results from Android Phone (with an account attached) and from standard Google SERP (without logging in to any account), we saw that the results seem to be roughly the same.
Setting the location at the Empire State Building, we’ve run a few searches and got the following evidence:

With results seemingly not biased to account attached, we spotted that some differences may occur depending on the number of “similar” places available around and the current time.
Understanding Local Voice Search Algorithms
With the knowledge of where various voice assistants gather their answers from, it’s easier to decipher what algorithms are behind each response.
Decoding the Google Assistant Algorithm
The Google Assistant’s algorithm is fairly straightforward — being a Google-run system, the assistant operates in line with the “traditional” local search logic.
In most cases, a voice-activated search for a local place to buy, eat or get some service, returns results from a Local Pack listing. The key advice for SEOs looking to optimize for visibility and market share across Google Assistant is to optimize for rankings within the Local Pack – voice search optimization services can assist with this.
Optimizing for Google Assistant via Local Pack
Our 2019 voice search study focused heavily on the ranking factors for Google Assistants.
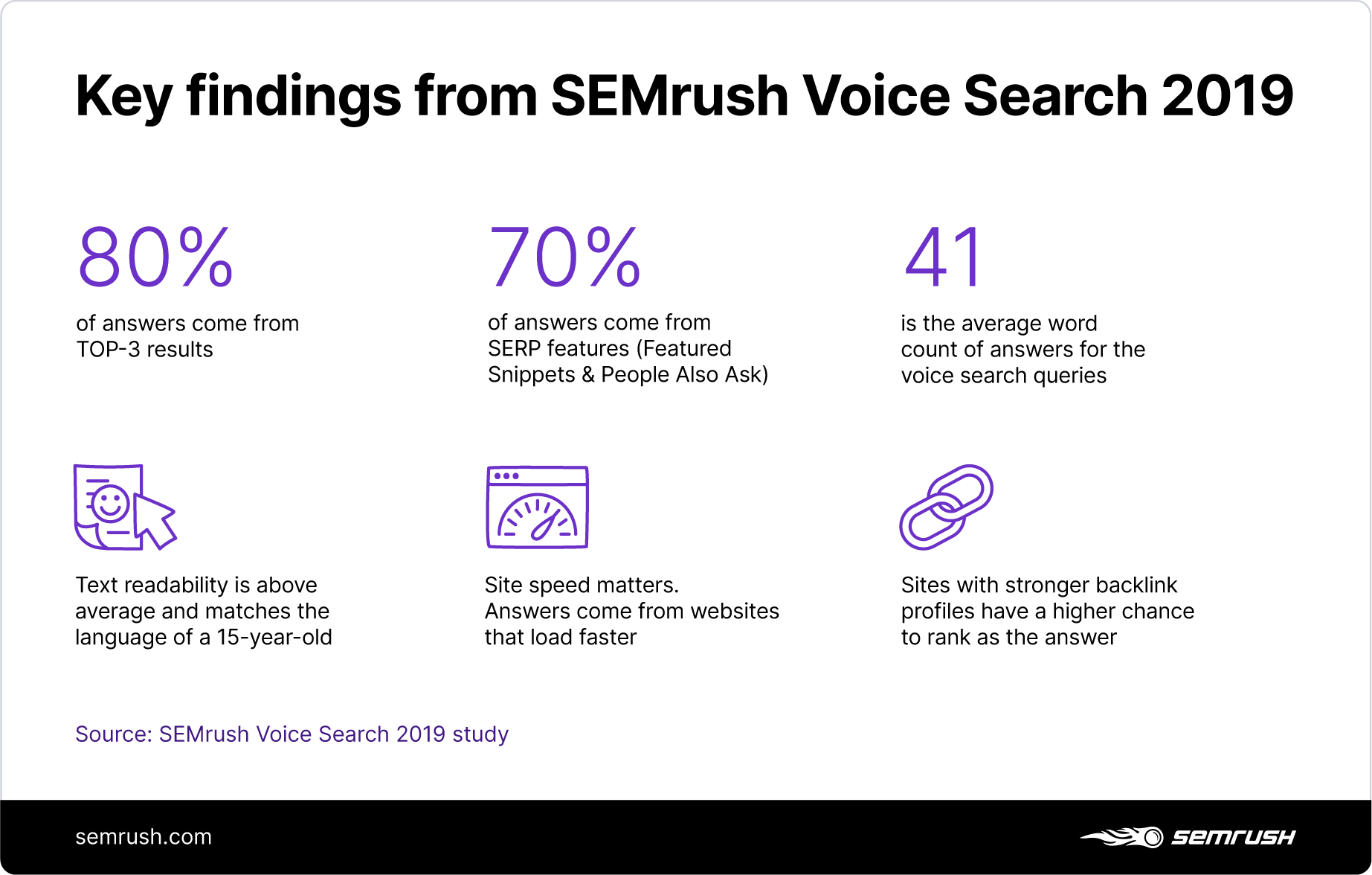
While the main factors influencing Google Assistant’s responses are still the page speed, ranking in the top three results, and occupying a Featured Snippet position, there are other things peculiar to local search.
To optimize for Google Assistant’s local voice search:
-
Polish up your business’s Google Business Profile: edit business info and make sure it’s consistent across every business listing on the web. Learn how to enhance your GBP in this post.
-
Make use of structured data: Gary Illyes shared during Semrush’s recent Marketing Scoop podcast episode that Google’s voice assistants are already using existing schema markups.
-
Create content that is simple and easy to understand: from targeting long-tail keywords to creating FAQ pages, tailor your site’s content to match the conversational tone of voice search. This post will walk you through this content optimization process.
If you were paying attention to actually writing for your users instead of machines, then I strongly believe that you are already optimized for voice search
Untangling the Siri Algorithm
If Google-run assistants take information from the Local Pack, Apple’s Siri operates differently.
Apple-run Siri is powered by Apple Maps that take business information from Yelp. Siri reads aloud the answers displaying them on the device’s screen:

We spotted that there are four main factors (listed in the order of importance) that influence the voice assistant’s response:
-
Distance
-
Number of Reviews (Yelp)
-
Star rating
-
Pricing coefficient (usually shown as a set of dollar signs)

Siri Ranking Factors Observations
Taking a specific case, when Siri returns results for a “restaurant near me” search, the process appears to be as such:
-
Siri looks for the local restaurant listed on Apple maps.
-
The assistant shows the closest one, suggesting that distance is the key factor when asking ‘near me’ queries.
-
It gathers business info from Yelp, TripAdvisor, or opentable.com (if applicable) along with the average star rating and the number of reviews. If there are multiple data sources, Siri prioritizes Yelp.
In the case of “best restaurant” search:
-
Siri shows restaurants with the highest average star rating, with distance not playing a role for the returned results.
-
Siri pays less attention to the number of reviews for a place, prioritizing the star rating. An unpopular place with only one 5-star review can win over a more trending spot with a 4.5-star rating.
For a “best restaurant near me” search, Siri will return the same results as in the previous case, suggesting that the keyword “best” is more valuable than the keyword “near me”:
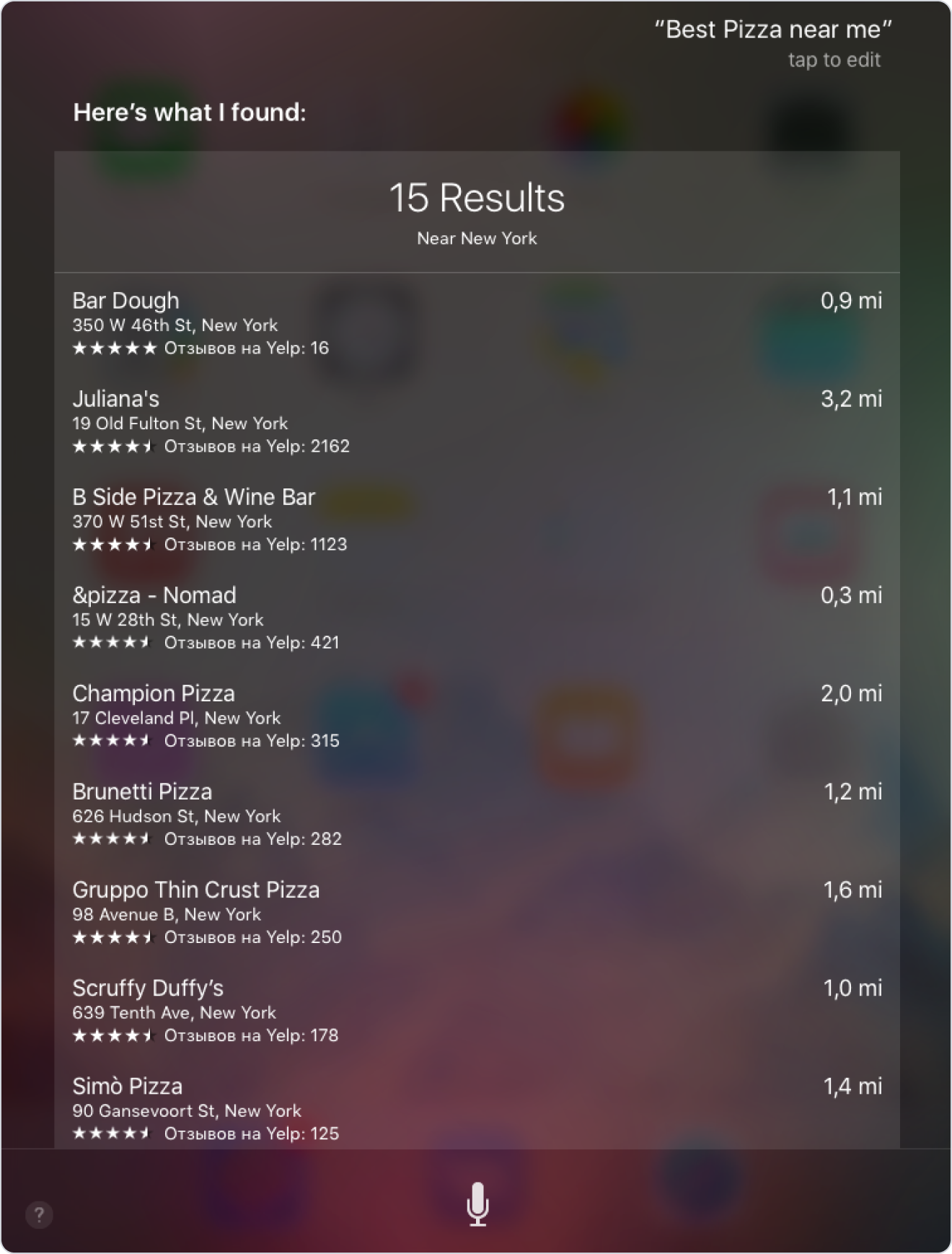
If the search has anything to do with queries related to Apple (e.g. “where to buy Airpods”), Siri only suggests a visit to apple.com.

Optimizing for Siri
There’s hardly anything to do about the distance factor. The key to optimizing for Siri is to roll out a strategy for collecting great reviews in higher numbers than other local competitors.
To take a higher spot on Yelp and the top position in Siri’s response, businesses should:
-
Consistently work on generating new high-star reviews on Yelp. This online reputation guide includes tips on how to encourage positive reviews from customers.
-
Optimize the Yelp listing by:
- Filling out as much information as possible on their Yelp profile;
- Choosing the most relevant category to be listed under. Using the wrong category can noticeably hurt Yelp rankings, which affects Siri visibility;
- Adding photos as Yelp allegedly gives preference to listings that include more images;
- Optimizing the listing’s content in-line with the target keywords;
- Keeping the listing updated, refreshing business information and replying to customer reviews.
Summary

2020 Voice Search Study’s Methodology
Employing 6 devices that run on Google, Siri, and Alexa voice-activated assistants, we asked 5,000 questions to:

-
Google Home
-
Google Home Mini
-
Google Home Hub
-
iPad Mini 1 (Siri)
-
Amazon Echo (Alexa)
-
Android Phone
The exact questions were defined with the help of Semrush’s Keyword Magic tool that sorted the questions by search volume to help us focus on the most popular queries and most frequent combinations.
The questions fell into several base types and combinations.
Base questions:
-
Where to <entity> (e.g. “where to buy pizza”)
-
<entity> near me (e.g. “pizza near me”)
-
Best <entity> — (e.g. “best pizza”)
-
<entity> delivery — (e.g. “pizza delivery”)
Combination questions:
5. Best <entity> near me (e.g. “best pizza near me”)
6. Other combinations — (e.g. “best pizza delivery near me”)
All the devices used within this study were set to the same location to get a conclusive answer.
To uncover the Google Assistant's algorithm:
We recorded the answers for each query from every device. Using the Keyword Magic tool that keeps Google’s SERP, we cross-matched them against the search results users receive from a regular desktop search.
To untangle Siri’s algorithm:
-
We gathered the answer results to a series of search queries from Siri, automatically retrieving the text data from the screenshots that we took.
-
We collected the link on the Yelp page of each result (where possible) as well as the Yelp data for each place on the screenshot (if the name and address were stated).
-
Following this, we collected the list of places at the location.
-
For each institution, we could collect name, rating, price, food tags (for restaurants), and reviews.
To build the ranking model, we took the first 3 positions for each query to enable a comparison.
Special notes
Smart speakers are being used for more than voice search, with many using these devices to control smart tech around the house, play a song, or set a timer.
Apple Homepod and Amazon Echo (Alexa) are largely home-based devices. With a pre-built database of answers to popular queries like “who is Elon Musk?”, they are primarily intended for voice commands and questions on general topics, rather than specific local search queries.
To get more accurate data for further analysis, we only left Amazon Echo, disregarding Apple Homepod, to be a part of our study.
Final Words
Optimizing for voice search is hardly a matter of choice as more users turn to assistants for local searches. With voice search sales projected to reach $40 billion, businesses investing in voice search optimization can expect to see tangible results.
Lionbridge’s success story is only one proof. After the company started optimizing for voice search, it saw 25% of tracked keywords reaching the top 3 SERP positions, and a 46X growth in the number of obtained Featured Snippets. As a result, they gained a 127% traffic increase YoY.
Voice search also offers opportunities for local businesses that struggle to get to the top 3 SERP positions and obtain a Featured Snippet. Proximity and the range of assistants using different search algorithms — not just Google’s ranking logic — can play to their favor and help them get a spot in Siri’s or Alexa’s response.
