Understanding each HTML tag is a crucial step to implementing your own HTML code.
Use this guide as a reference for standard HTML tags and how to use them.
What are HTML Tags?
HTML tags are simple instructions that tell a web browser how to format text. You can use tags to format italics, line breaks, objects, bullet points, and more.
These tags live in the HTML (or the Hypertext Markup Language) of every webpage. Simply put, HTML is the language of web pages.
Examples Of HTML Tags
<p> Paragraph Tag </p>
The <p> and </p> are the HTML tags and “Paragraph Tag” is the HTML element, i.e. the on-page text.
This tag formats any text between the opening <p> tag and the closing </p> tag as a standard paragraph or main body text.
<h2> Heading Tag </h2>
In this example, <h2> and </h2> are the HTML tags and “Heading Tag” is the HTML element, i.e. the on-page heading.
Using this tag will format any text between the opening <h2> tag and the closing </h2> tag as a Heading 2 (a type of subheading.)
<b> Bold Tag </b>
Here the <b> and </b> are the HTML tags and “Bold Tag” is the HTML element, i.e. the on page text.
This tag will format any text between the opening <b> tag and the closing </b> tag as bold.
<i> Italic Tag </i>
Here, the <i> and </i> are the HTML tags and “Italic Tag” is the HTML element (the on-page text.)
This tag will format any text between the opening <i> tag and the closing </i> tag as italic.
<u> Underline Tag </u>
Here the <u> and </u> are the HTML tags and “Underline Tag” is the HTML element, i.e. the on page text.
This tag will format any text between the opening <u> tag and the closing </u> tag as underlined.
How to Check Your Site’s HTML Tags
If you already have HTML tags on your web pages and want to check if they’re used correctly, you can do so by looking at the HTML of your page. To do this, all you need is your web browser.
To view your webpage’s HTML, you should:
- Right-click while on your webpage in Google Chrome
- Click “Inspect”
- You'll see the HTML code in a box at the side or bottom of your page
- Use Ctrl + F to find particular tags or elements
Not sure what you’re looking for? Try the Site Audit tool.
To check if your website uses HTML tags correctly, you can do an SEO audit of your site. The Site Audit toolcan check if the basic HTML tags and attributes are correct and if your pages use too much HTML.
To perform an SEO audit with the Site Audit tool, you’ll need to create a project for your domain first.
Pro Tip: Sign up for a free account to follow along.
The tool will prompt you to enter your target domain:
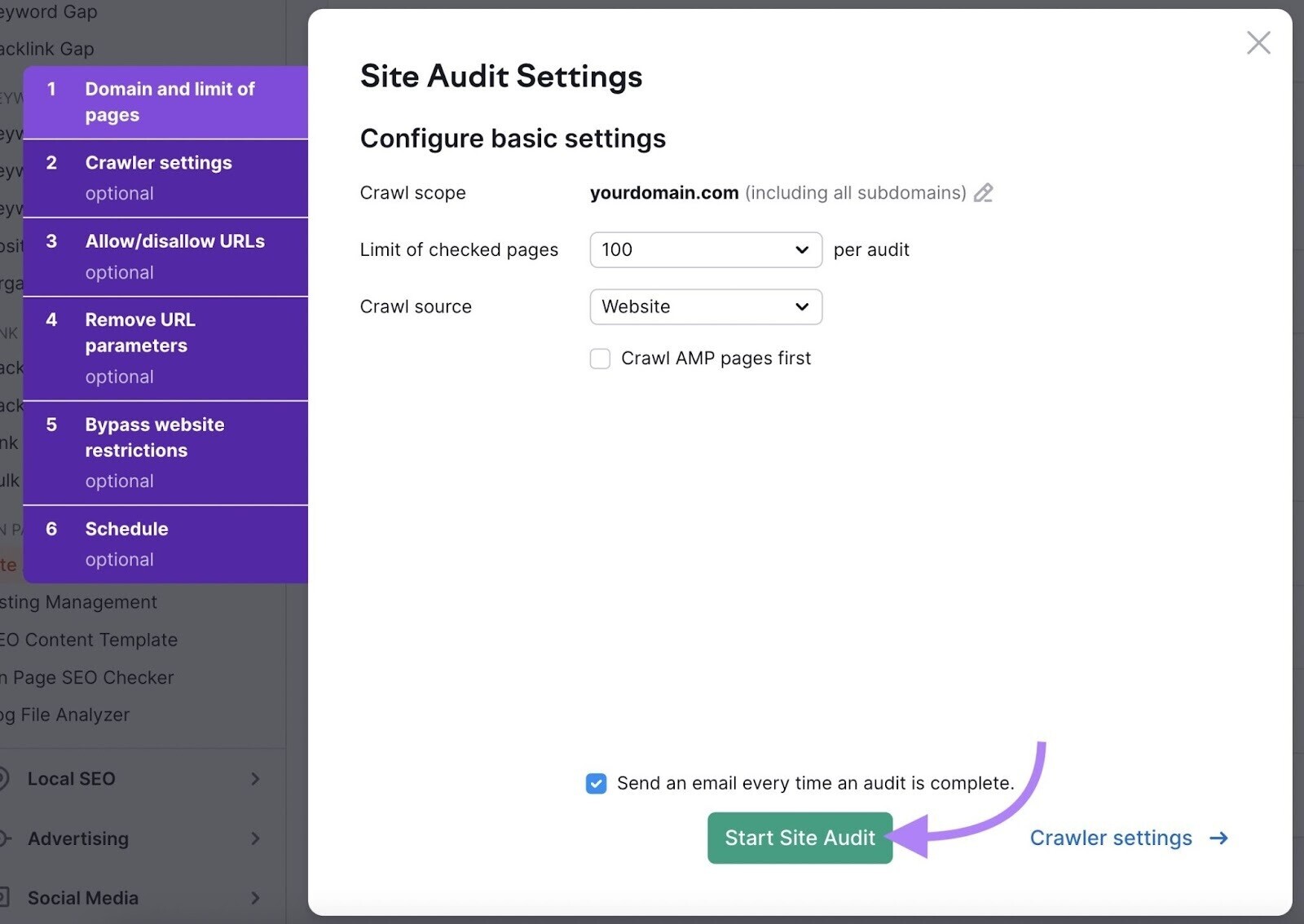
Then, configure any additional settings, such as focusing on a particular subdomain, subfolder, or specific list of URLs:
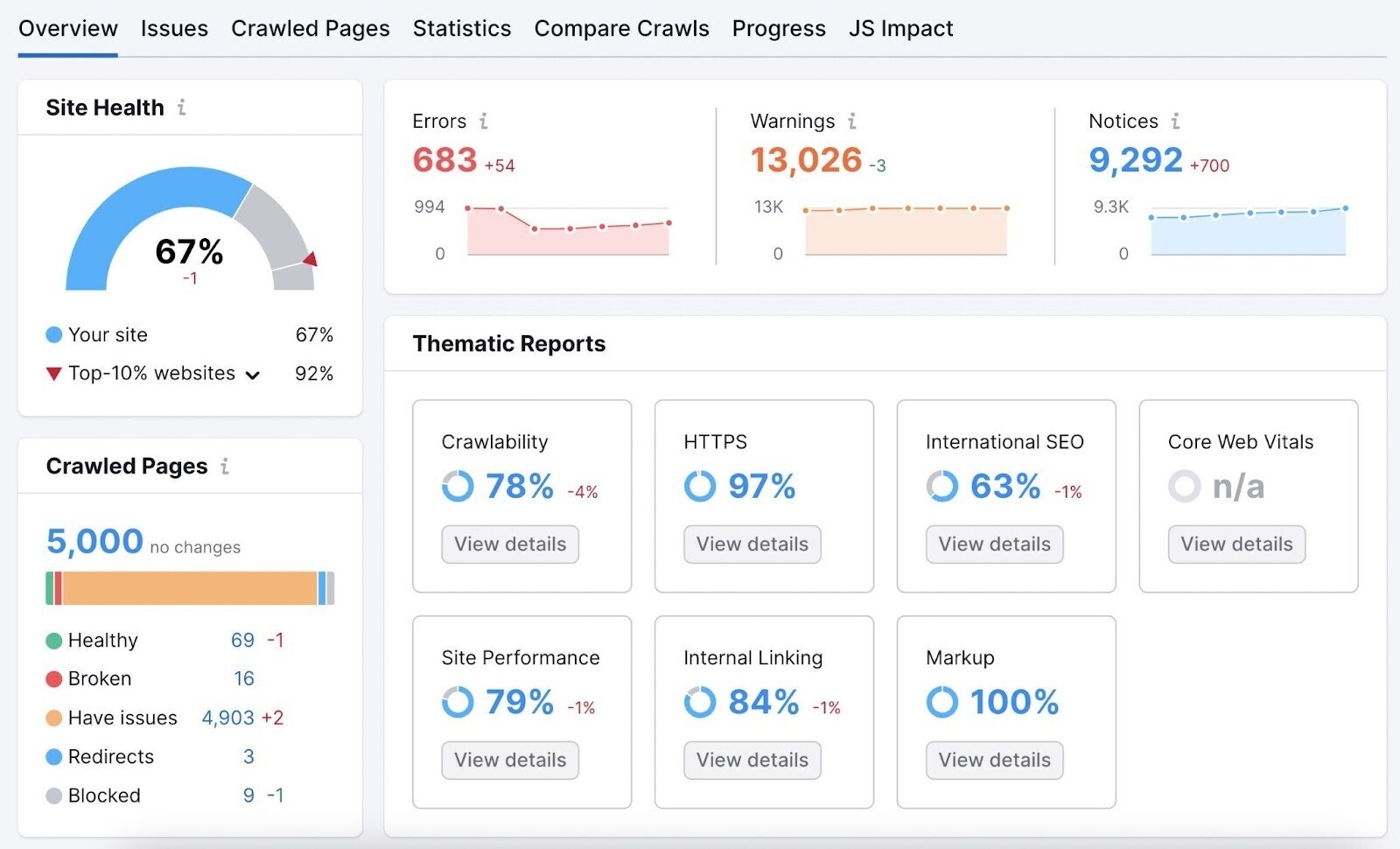
Once the audit is complete, you’ll be directed to the Site Audit overview report, where you’ll have a high-level view of any site issue:
Select the “Issues” tab for a more detailed view of any HTML issues. In the search bar, you can search for “HTML,” “H1,” or any relevant HTML tag to drill down to specific HTML tag issues.
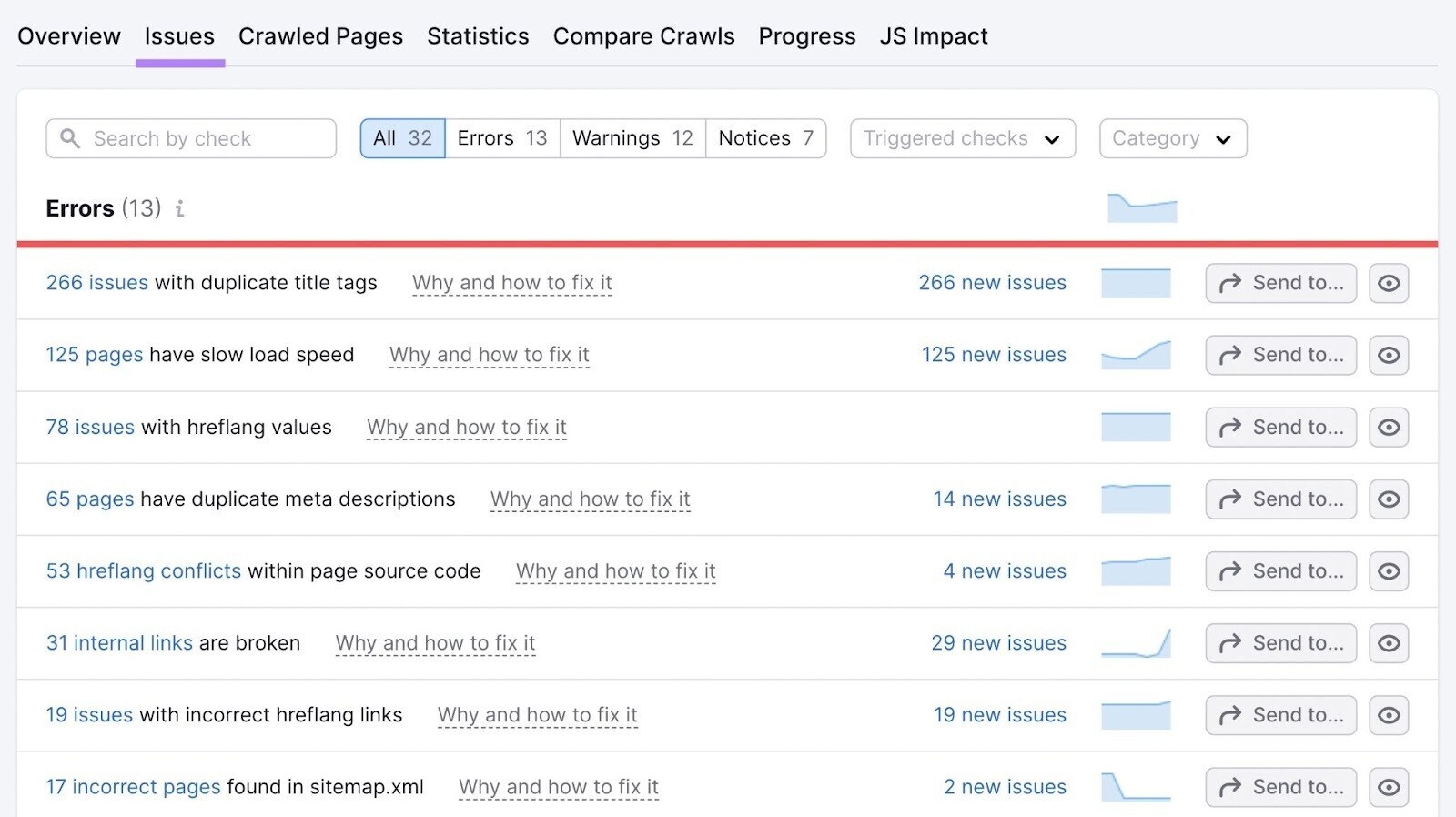
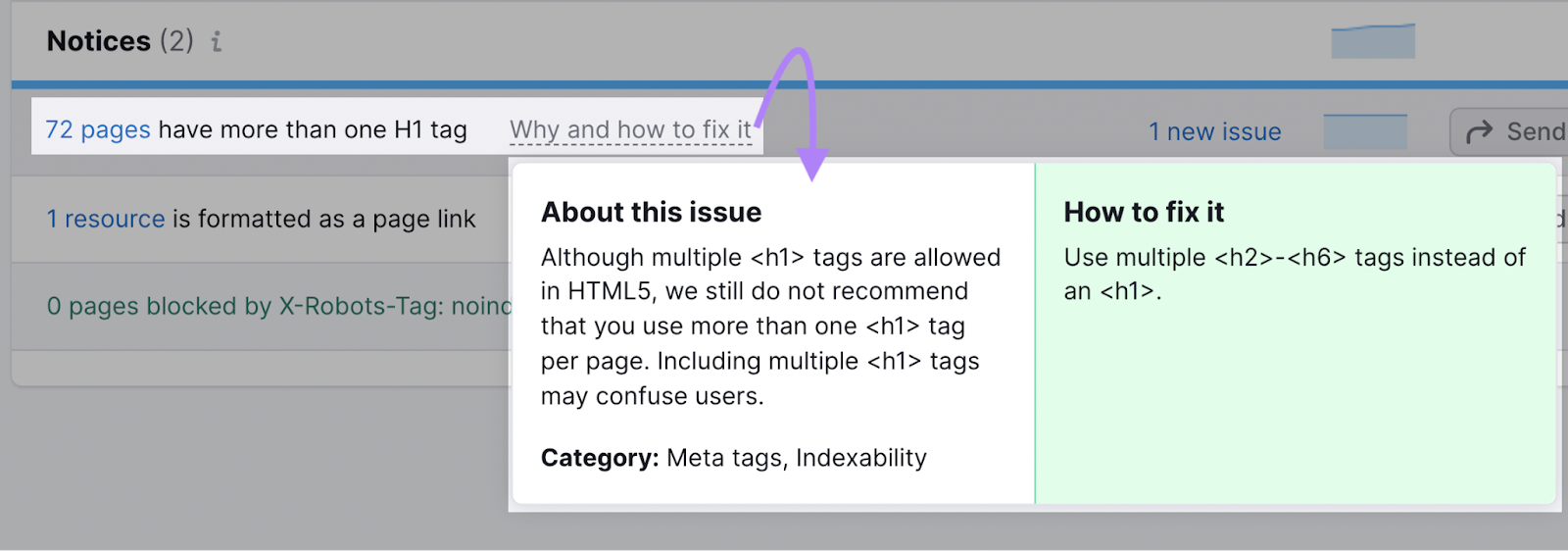
The tool also provides suggestions on how to fix each issue:
How Do Web Pages Read HTML Tags?
Servers read HTML code to understand and render content. It will read the HTML from top to bottom, much like how you’re reading this guide.
You can use as many or as few tags as you like to format content. However, there are a few essential HTML tags and rules you’ll need to follow.
An HTML tag must contain three parts:
- An opening tag — this will start with a < > symbol
- Content — the short instructions on how to display the on-page element
- A closing tag — this will end with a </ > symbol
However, some HTML tags can be unclosed. That means that the HTML tag does not need to be closed with a </ >. You’ll typically use unclosed tags for metadata or line breaks.
What’s the Difference Between Attributes and HTML Tags?
Although this guide is all about HTML tags, it’s important to know the difference between HTML tags, elements, and attributes.
An HTML element is an item on the page; it’s part of the web page’s content. An HTML tag affects how an HTML element appears. An HTML attribute describes the characteristics of that element.
Here’s a breakdown of how elements, tags, and attributes work together:
- HTML tags contain instructions on how to display an on-page element. They begin with a < and end with a > and precede and follow the content of the element. (e.g <b> Bold Tag </b>)
- HTML Elements are the on-page content sandwiched within the tags. (<b> Bold Tag </b>)
- HTML Attributes provide additional information about HTML elements and appear at within the HTML tag (e.g. <html lang="en-US">).
| Type | HTML Tags | HTML Elements | HTML Attributes |
| Contains | Instructions on how to display an on-page element | The on-page content to be displayed | Additional information about the on-page elements |
| Appearance | It starts with < and ends with > | Sandwiched within an HTML tag | Appear in the starting tag before any elements |
The Most Common HTML Tags
There are nearly 100 different types of HTML tags that you can use for your web pages. Here is a list of the most common HTML tags:
| Tag | Type | What It Is |
| <p> | HTML Text Tags | Paragraph |
| <h1> | HTML Text Tags | Heading 1 |
| <h2> | HTML Text Tags | Heading 2 |
| <h3> | HTML Text Tags | Heading 3 |
| <h4> | HTML Text Tags | Heading 4 |
| <h5> | HTML Text Tags | Heading 5 |
| <h6> | HTML Text Tags | Heading 6 |
| <strong> | HTML Text Tags | Strong |
| <em> | HTML Text Tags | Emphasis |
| <abbr> | HTML Text Tags | Abbreviation |
| <address> | HTML Text Tags | Contact Information |
| <bdo> | HTML Text Tags | Override The Current Text Direction |
| <blockquote> | HTML Text Tags | Content From Another Source |
| <cite> | HTML Text Tags | Title Of The Work, Book, Website |
| <q> | HTML Text Tags | Inline Quotation |
| <code> | HTML Text Tags | Display A Part Of Programming Code |
| <ins> | HTML Text Tags | Text Inserted |
| <del> | HTML Text Tags | Text Deleted From The Document |
| <dfn> | HTML Text Tags | Term Defined Within A Sentence/Phrase |
| <kbd> | HTML Text Tags | Keyboard Input |
| <pre> | HTML Text Tags | Preformatted Text |
| <samp> | HTML Text Tags | Sample Output Of A Computer Program |
| <var> | HTML Text Tags | Variable Name Used In Mathematical Or Programming Context |
| <br> | HTML Text Tags | Single Line Break |
| <div> | HTML Text Tags | Division |
| <a> | HTML Link Tags | Anchor Tag For A Link |
| <base> | HTML Link Tags | Base Url For All Relative Url Within The Document |
| <img> | HTML Image And Object Tags | Image |
| <area> | HTML Image And Object Tags | Area Of An Image Map |
| <map> | HTML Image And Object Tags | Image Map |
| <param> | HTML Image And Object Tags | Parameter For An <Object> Element |
| <object> | HTML Image And Object Tags | Embed An Object |
| <ul> | HTML List Tags | Unordered List |
| <ol> | HTML List Tags | Ordered List |
| <li> | HTML List Tags | List |
| <dl> | HTML List Tags | Description List |
| <dt> | HTML List Tags | Term In Description List |
| <dd> | HTML List Tags | Definition/Description Of A Term In Description List |
For a full list of all 100+ HTML elements, visit this helpful guide from javaTpoint.
Final Thoughts
Understanding HTML doesn't have to be complicated. With the cheat sheet in this guide, you should identify and implement HTML tags for your web pages.
Need more details on HTML attributes and how to fix them? Try our guide to HTML Attributes.
For more information about doing a site audit and checking your site’s HTML, check out our guide to doing a full SEO audit in 18 steps.
