The evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) has witnessed remarkable recent advancements that keep pushing the boundaries.
Game-changing AI models like ChatGPT are clear proof of how AI technology is increasingly closing the gap between machine intelligence and human cognition. And of its unprecedented global impact across multiple industries.
In this article, we explore 15 trends in AI set to redefine business operations in 2024.
We’ll also advise you on how to stay ahead of the AI curve to maximize business opportunities—including using Semrush tools to monitor AI trends.
1. Impact of AI on Jobs
AI may transform the job landscape by cutting roles in some sectors, increasing them in others, and augmenting existing ones with more advanced capabilities.
Respondents of the Future of Jobs Report 2023 “anticipate a structural [labor] market churn of 23% of jobs in the next five years.”
Most of these positions will likely have well-defined processes and low complexities. Here are a few at-risk work scenarios we anticipate:
- Intelligent robocalling solutions could replace in-person telecalling jobs
- AI-based accounting software could render bookkeeping roles redundant
- A combination of bots and AI-based software could phase out retail sales associates
- Smart AI assistants could see companies do away with human personal assistants and receptionists
- Specialized AI-based underwriting programs could replace insurance underwriters
That said, more knowledge workers are increasingly enhancing their skill set with AI-based solutions. These solutions can aid with brainstorming ideas, copywriting, video editing, and image creation.
AI solutions already help medical professionals synthesize patient information and lawyers match patterns of new cases against old ones.
Some systems reduce the workload of customer service representatives by automating most interactions. Specialized AI machines augment human capabilities in manufacturing and research labs.
In addition, AI is poised to create further new jobs that help businesses apply AI.
For instance, we’ll need more AI artists, content creators, and research scientists. Plus machine learning engineers, deep learning engineers, and data scientists. As well as AI chatbot developers, AI product managers, AI solutions architects, and chief AI officers.
2. AI in the Workplace
People can begin to use AI in their workplaces to perform HR, marketing, and production tasks.
HR employees could use AI to source, shortlist, schedule interviews with, recruit, and onboard new candidates with greater efficiency.
Each industry can also find ways to maximize its use of AI differently. Like employing a technology like AI-based computer vision (CV).

Image source: N-iX
CV could help manufacturing companies spot assembly line errors. The retail industry will probably develop CV applications to manage inventory. Insurance companies may use CV on drones to visually inspect damaged property claims.
And so on.
3. Augmented Workforce
You can combine technologies such as AI, CV, and virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) to improve key business outcomes.
Employees could soon work with digital humans, bots, and AI assistants to perform daily business operations. For example, it may soon be possible for employees to instruct digital humans via chat.
We’ll likely also see AI-based assistants carry out the bulk of customer service tasks daily. While employees monitor performance and step in only when needed.
4. AI-Augmented Apps
Both new and existing apps will add AI capabilities to enhance the user experience and expand functionality. AI-augmented apps will continue to introduce new features and use cases for existing tools.
Gartner predicts that the percentage of new apps using AI will grow nearly sixfold by 2026.
Consider an app like Grammarly as an example of an online editing and writing tool that’s becoming increasingly augmented with AI.

In 2023, it announced new AI-powered features. Today, the tool uses AI to perform real-time analysis of users’ unique habits and writing styles to make personalized recommendations.
Similarly, the AI companion chatbot Replika helps businesses to meaningfully engage with their customers.
The app uses natural language processing (NLP) and large LLMs to understand user queries and answer in a conversational tone.
Another example of AI-augmented software is FaceApp. Using artificial intelligence to transform facial expressions and features in photos, it can change or add hairstyles, makeup, age progression, and even smiles.

The app’s AI algorithm analyzes your facial features and applies realistic transformations. Showcasing the capabilities of AI in image processing and editing.
With so many nuanced uses of AI currently, AI-augmented apps will inevitably continue to be a trending feature.
5. Personalization at Scale
AI can enable businesses to understand individual user needs and serve personalized experiences at scale.
More businesses will provide AI-powered product, service, and content recommendations to customers. Which could help increase revenue and customer loyalty.
AI has been available for large technology companies for many years. Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify deliver personalized content to hundreds of thousands of users through AI.
These platforms’ AI algorithms automatically analyze viewing or listening histories to then suggest movies, shows, or music that align with a user’s tastes.
Similarly, ecommerce platforms like Amazon now use AI to analyze customer browsing and purchase history. They can then provide personalized product recommendations, enhance shopping experiences, and increase sales opportunities.
The technology that serves these tech giants is bound to become more widely available to smaller businesses.
In the future, independent retailers and upstart tech companies could offer many of those same AI features to engage and convert customers.
6. AI-Driven Customer Service
Customer service will use AI to understand customers’ preferences and provide highly personalized assistance.
Some companies have already started their AI-driven customer support process.
For example, the automated accounts payable (AP) company Stampli introduced Billy the Bot.

The in-platform AI helps the customer through AP processes and answers questions along the way.
As AI-powered chatbots and specialized large language models (LLMs)—which understand and generate text—begin to understand your business operations, they will start having independent conversations with your users.
Further reading: Learn more about LLMs and other types of AI models with our comprehensive guide.
Modern customer service solutions will synthesize key behavioral information about each customer from their interactions with your app, website, chatbot, email, and social media. Then use this data to create highly personalized interactions with users.
Soon, AI-driven customer service solutions could greet a new website lead from Florida with a “Nice to meet you on this sunny day” message.
Or help your users troubleshoot without requiring them to provide context or additional details.
And even automatically generate code to help users integrate your solution with other apps and tools.
7. AI-Based Marketing
Marketers will increasingly adopt more AI tools to run lean marketing operations, create SEO content, and repurpose existing content.
For instance, AI assistants such as Google Assistant, MarketingBlocks, and ChatGPT can organize to-dos, create marketing assets, and perform research—helping you achieve more with fewer resources.

An AI-powered SEO tool like ContentShake helps marketers create search-optimized content that ranks higher in search results.
Similarly, Semrush’s SEO Writing Assistant helps you spot SEO enhancement opportunities across your content.
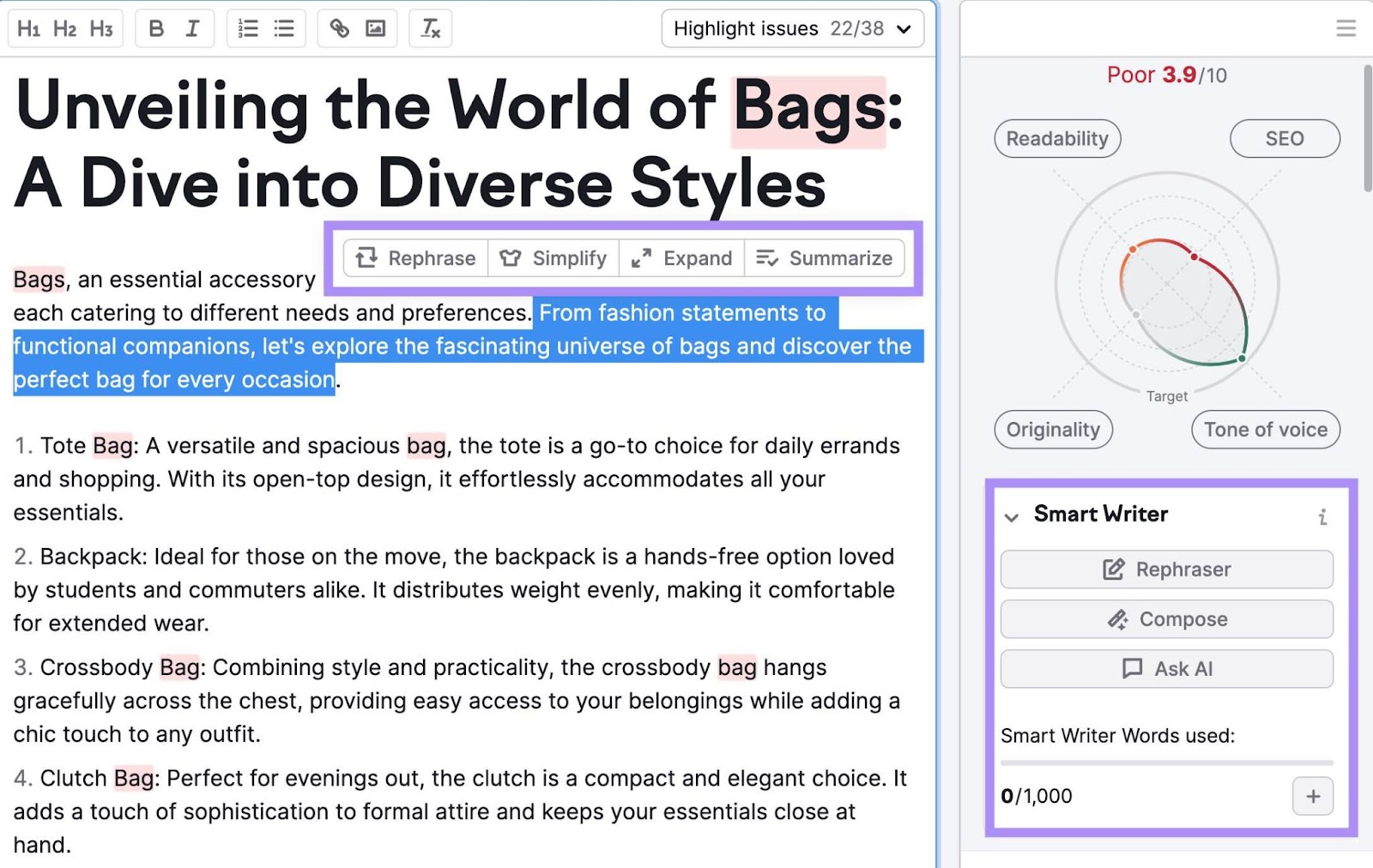
You also have the option to boost your content marketing efforts using AI rewriting tools to repurpose your existing content.
Further reading: Boost Your Content Output: 11 of the Best AI Rewriting Tools in 2024
8. Generative AI
Businesses are increasingly using generative AI tools to create new text, images, and videos because they can save time and cost.
Individuals and businesses leverage AI tools like ChatGPT and Jasper, which help users fashion blog posts, video scripts, song lyrics, and even poems.
As users become more comfortable with generative AI, they’ll likely explore producing other forms of media as well.
AI image generators allow users with no design skills to create visual media from text descriptions.
For instance, input a prompt such as “writing a story in a modern home office using AI” in DALL-E. OpenAI’s text-to-image model will generate an image output similar to this:

This trend is likely to spill into specialized and skilled work, too.
The AI picture trend, also known as the AI face trend, gives professional photographers and designers a run for their money. People can quickly post AI-generated photos of themselves, friends, celebrities, and fictional characters on their social platforms.
Further reading: Find out which top 6 AI image generators we recommend.
Then, there’s video content.
A recent TikTok AI trend makes it easy for anyone to turn popular cartoon characters into funny memes. So TikTok users can create memes faster.
Likewise, the recent AI Instagram trend helps creators scale their content. For example, AI-based video editing tools let you cut a long interview into small and engaging short videos to repurpose on Instagram without much manual effort.
Generative AI adoption will likely continue to grow. The quality of the content will continue to improve. And users will explore using AI to generate content in more formats and media.
9. Multimodal AI Models
Businesses will use multimodal AI models to process and generate text, images, audio, and video outputs more efficiently.
Imagine a multimodal AI robot that can read your newspaper, summarize it for you in a pleasant tone over breakfast, and search online for answers to all your follow-up questions. Such a robot might be based on multimodal AI models.
A few recent multimodal AI model developments include:
- LLaVA: An open-source large multimodal model (LMM) jointly developed by the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Microsoft Research, and Columbia University. It offers an open-source version of a multimodal GPT-4. Its health care-focused variant, LLaVA-Med, can respond to biomedical image inquiries.
- ImageBind: An open-source model created by Meta. The algorithm aims to mimic human perception while ingesting text, images, videos, audio, 3D measurements, temperature data, and motion data.
- SeamlessM4T: This algorithm designed by Meta excels in translation and transcription tasks. It supports various forms of communication like speech-to-speech, speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and text-to-text translations.
10. AI-Powered Software Engineering
Integrating AI in software engineering can enhance developer creativity, improve code quality, and make the development process more efficient.
Some use cases for AI in software engineering include generating working unit tests—automation developers use to test new code and find errors or bugs.
For example, software engineers can use GitHub Copilot to write unit tests that would make sure a piece of code correctly handles text that a user types into a form.
Thomas Dahmke, CEO of GitHub, says the AI era is already upon us.
Developers have arrived in the age of AI. The only question is, how fast do you get on board? Or are you going to be stuck in the past, on the wrong side of the “productivity polarity?
AI can also convert code from one language to another and maintain large software systems. LLMs like ChatGPT can interpret and help maintain code for large-scale software systems.
It’s especially effective when paired with a model-driven development (MDD) approach, which lays out the basic “blueprint” for how the code should work before the code itself is actually written. LLMs can use this “blueprint” to analyze written code or generate code from scratch to meet the stated requirements.
AI tools can also assist developers in creating data schemas and generating test data based on schema information.
They can also process large amounts of data and provide recommendations that reduce data handling costs.
11. Quantum AI
Quantum computing and AI will advance each other to solve complex computation problems beyond classic computers’ capability.
When quantum computing hardware is coupled with AI, it significantly outperforms hardware and software capabilities in tasks involving speech recognition, complex decision-making, and big data analysis.
We’re already seeing the application of quantum computing with AI—in modeling high-resolution weather forecasts, assessing financial risks, and developing new drugs.
We foresee that quantum AI will continue to have more such real-world applications in 2024 and beyond.
12. AI Design Trends
We anticipate AI in UI and UX (user interface and user experience) design and 3D animation to be the top AI design trends in 2024. Incorporating AI into UI and UX design processes will help designers make better data-driven decisions.
Further reading: 10 UX Design Examples to Get Inspired
For example, designers can use a tool like Lookback to gather detailed data about user actions, heat maps of their mouse movements, and click-through rates (CTRs).
Designers can combine the data with an intelligent AI program like Adobe Sensei to synthesize thousands of user data points into actionable UI/UX design directives.
3D animation designers will also increasingly use AI-based algorithms to create detailed visual effects, environments, and characters.
For instance, 3D animators could use what are known as procedural modeling algorithms to help create content for movies, video games, and more.
These algorithms are essentially a set of rules about content creation that the computer follows.
Rather than spending their time creating new content from scratch, 3D modelers can focus on setting the rules and let the algorithm generate image or video content.
The company DeepMotion uses AI to capture real-life movements and generate virtual content.
Here’s an example of its Animate 3D creating an animation based on the movement shown in a video:

13. Digital Humans
Businesses could use cost-effective, customizable digital humans as sales assistants, corporate trainers, and social media influencers. These digital humans will soon look, behave, and even think like humans.
AI tools like Synthesia already help businesses create digital humans.
Some common use cases include corporate trainers, employee induction presenters, and virtual assistants.
For example, you could use digital humans to train your new and existing sales reps.

Virtual influencers are another emerging use case for digital humans.
Take the AI influencer Aitana from The Clueless agency. She now represents various business brands, earning up to €10,000 ($10,800) a month from advertisements and brand endorsements.
Instead of holding ad photoshoots, you just need designers to Photoshop the ads. Over 283,000 followers await Instagram updates from the virtual influencer.
Rubén Cruz, The Clueless founder, describes how they put Aitana together:
A lot of thought has gone into Aitana. We created her based on what society likes most. We thought about the tastes, hobbies and niches that have been trending in recent years.
14. AI Regulation
Countries including Australia, India, Japan, and the UAE will likely soon announce new AI regulations—following the lead of the U.S., EU, and China.
Most governments are concerned about AI technologies’ lack of transparency and accountability.
For instance, the EU parliament released a provisional draft of AI rules on December 9, 2023. Here are its key features:
- Prohibitions on biometric categorization, recognizing emotions in places of work and study, scoring based on behaviors or personal characteristics, and exploitation
- Rules for general-purpose AI models that can have a huge impact on society
- Stricter transparency mandates for companies developing AI technologies
- Fines for AI violations of up to €35 million or 7% of an offending company’s annual turnover
Similarly, the U.S. passed an AI Bill of Rights in October 2022 that made a series of suggestions, including:
- Implementing protections against unsafe or ineffective systems
- Algorithms and systems not discriminating against humans in any way
- Users receiving protection against abusive data usage plus control over how their data gets used
- Users understanding how automated systems work and their impact
- Users’ ability to opt out and reach a human who can address any concerns
The U.S. followed the bill with an Executive Order on October 30, 2023. Mandating that AI developers and cloud providers share their safety tests and critical information with the U.S. government and related agencies.
The U.S. government will soon establish new safety and testing standards.
So far, unlike the EU or U.S., China has taken a more piecemeal approach to AI legislation.
China released laws on specific AI technologies. And regulated algorithm-based recommendation services—personalized product or service recommendations based on user profiles and behavioral data.
It also targeted deepfakes—AI-generated, realistic-looking content. Like videos of politicians, and celebrities saying or doing things they didn’t actually say or do.
We expect this scenario will change soon.
15. Ethical Considerations of AI
The world will likely debate the ethical ramifications of using AI more openly and widely. Discussions will revolve around topics such as copyright, safety, fairness, and accountability.
Businesses currently don’t have to report or disclose how their AI-based applications are trained. As a result, a few notable writers, software engineers, and artists have sued AI applications for turning original work into training datasets.
This copyright and intellectual property issue could worsen and force AI companies to change the way they build their tools and technology. And also create opportunities for new players to enter the market.
Will Douglas Heaven, senior editor for AI at MIT Technology Review, predicts new vendors and marketplaces will help address the concerns over copyrighted materials used to train AI.
New marketplaces will spring up around ethical data sets, and a cat-and-mouse game between companies and creators will develop.
Also, many AI activists question the reliability of AI programs to perform correct diagnoses and make proper decisions. A study shows that when radiologists were given AI diagnoses that were deliberately incorrect, their human accuracy fell below 20%.
Because AI programs are a black box, affected users won’t be able to hold anyone accountable for incorrect decisions.
AI can also perpetuate existing biases. For example, AI could generate content or make decisions based on racial stereotypes included in the training data.
So, safety, accountability, and fairness are bound to take center stage in future AI discussions.
Next, we outline what tools you can use to get all the relevant AI industry details to help your business stay ahead of the curve.
How to Monitor AI Trends With Semrush Tools
With Semrush, it’s easy to set alerts for all AI-related trends in TrendFeed. The app automatically sends you stories on the verge of going viral, along with fresh content ideas.
Once downloaded, access TrendFeed from the “App Center” tab of the tool dashboard, under “My Apps.”

Navigate different industries with the left-hand dropdowns.

Or use the text bar to search for something unique, like “AI in retail.” Click “Search” to get trending stories and feeds.

If you want to save a trending story, click “Save.” To explore and save a specific feed, click on the feed name listed under the story.
You can also use Semrush’s .Trends to identify AI trends happening in your industry based on your competitors’ marketing activity.
Under “.Trends,” click “EyeOn.”
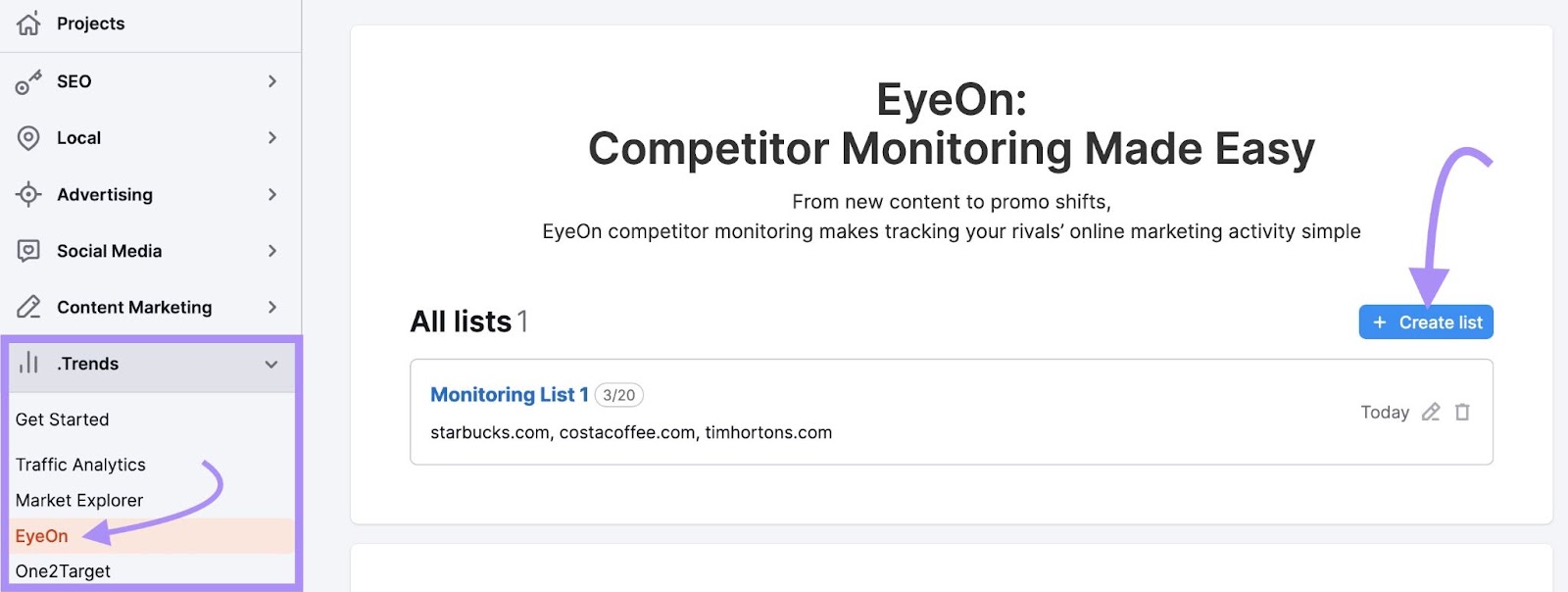
To compile a new list of competitor websites you want to monitor, click “+ Create list,” enter the domains in the “Competitors” field, and click the“Create” button.

EyeOn will generate regular reports about new blog posts, social media content, and other marketing activities by competitors.
Apply this process to research and monitor AI trends relevant to your business or industry.
